Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Contents
What is HPV
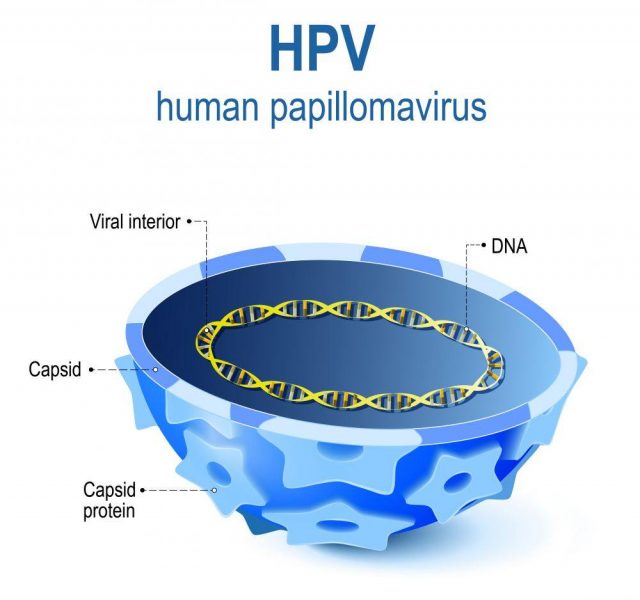
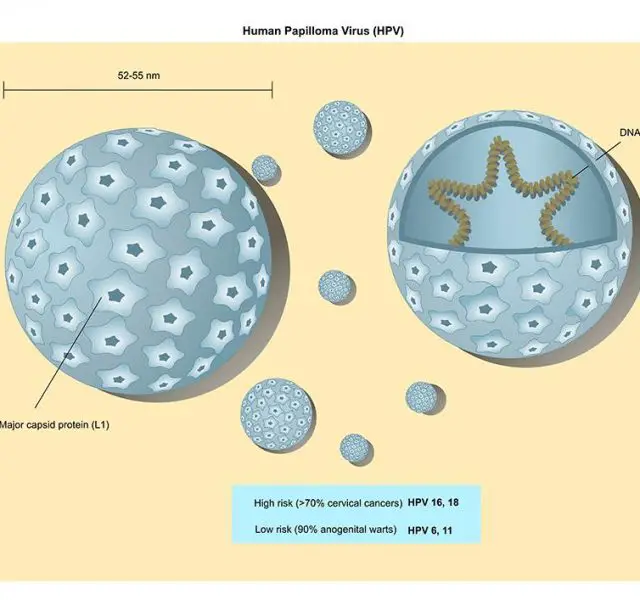
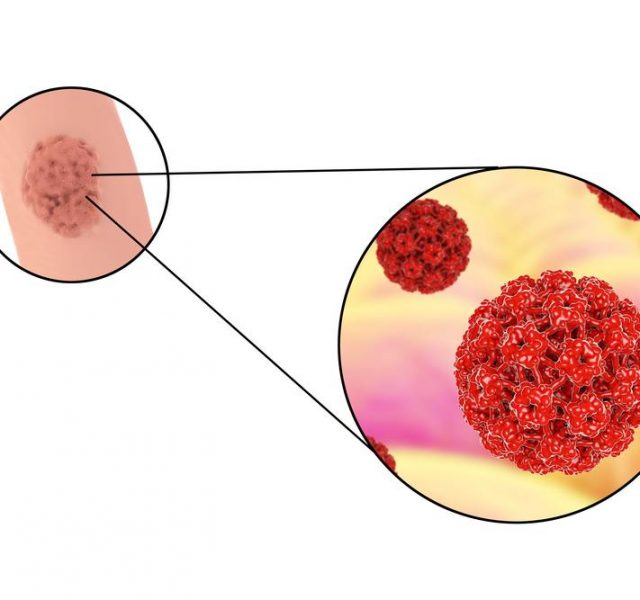
Human Papillomavirus, commonly referred to as HPV, is a vast group of viruses potentially leading to warts, genital warts and, in worst cases, cancer. However, most HPV types do not result in any harmful effect on human body, go away in several months and remain unnoticed. Sexually active people are more likely to obtain the infection and more than a half of all people acquire it over the course of life.
How is it Transmitted
Skin-to-skin contact is the typical way of transmitting HPV. Vaginal, anal, oral intercourse and other sexual contacts is the most common way of contracting the infection. It can also be passed through body fluids or mucous membranes.
Incubation Period
The problem with diagnosing human papillomavirus infection is its undetermined incubation period. In many cases HPV symptoms might show up within several months after the contact with infected person. However, as long as many patients might be unaware of the virus or the origin of it, it is difficult to name a certain incubation period.
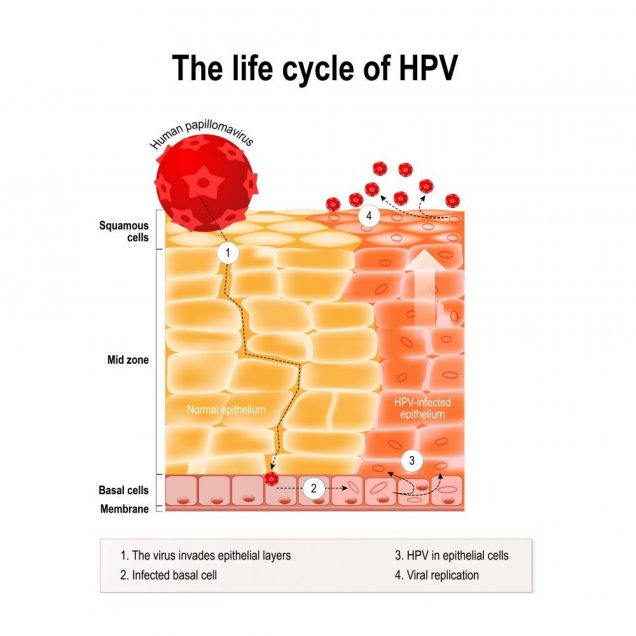
Life cycle of hpv in the human epithelium. hpv – Human papillomavirus infection which causes warts and cervical cancer (carcinoma of Cervix) – Malignant neoplasm arising from infected epithelial cells
Symptoms and Signs of HPV
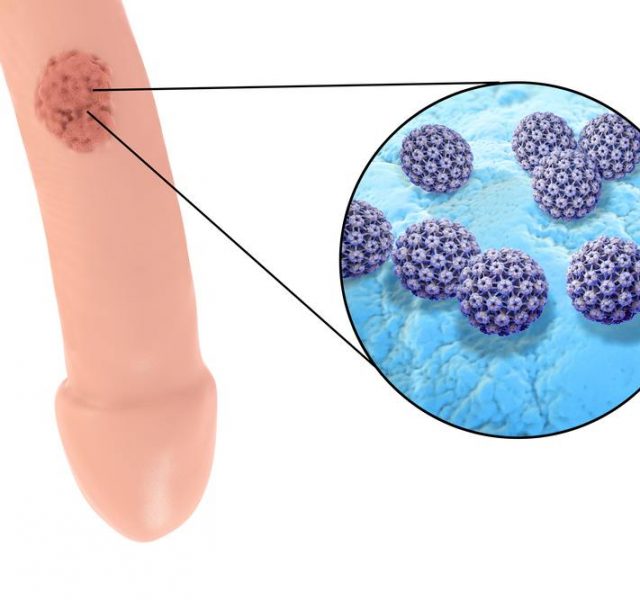
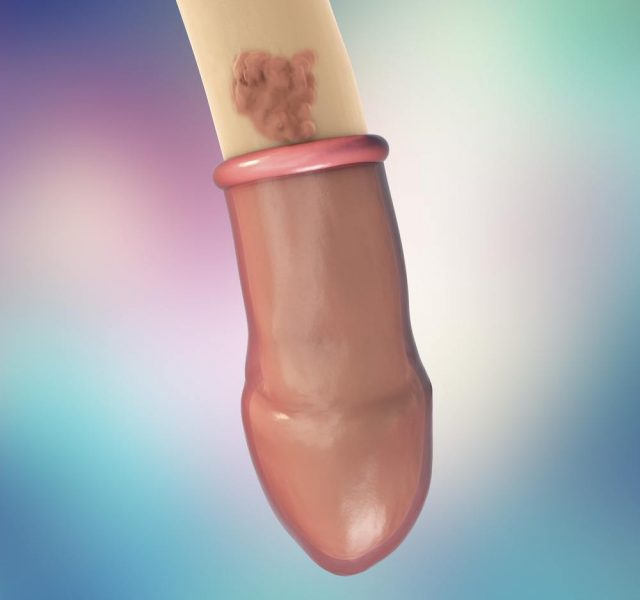
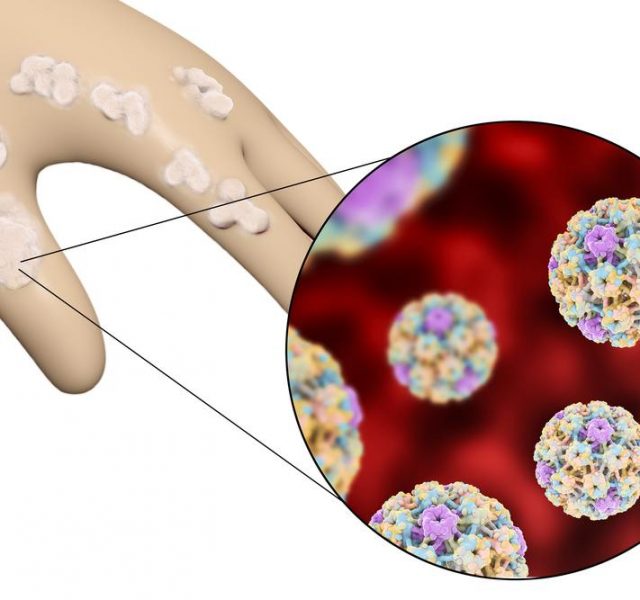
Most HPV types have no symptoms and disappear without doing any harm to human body. However, several virus types cause genital warts, which is a direct sign of carrying a virus. Some types affect feet, hands, and, rarely, throat and mouth. The color of warts may vary from flesh to pink, they can have cauliflower look.
HPV Symptoms in Men
Genital warts normally appear on penis, scrotum, anus or rectum.
HPV Symptoms in Women
Vulva, vagina, cervix, anus and rectum are the common areas affected by genital warts.
Click here to see all STD Symptoms.
HPV Testing
Human Papillomavirus is known to be affecting women rather than men so they need to pay additional attention to the infection, as it might cause cervical cancer in certain cases.
HPV Testing In Women
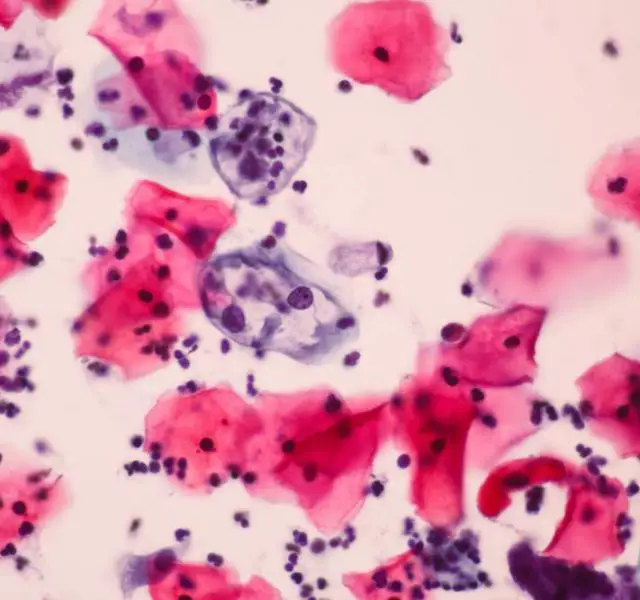
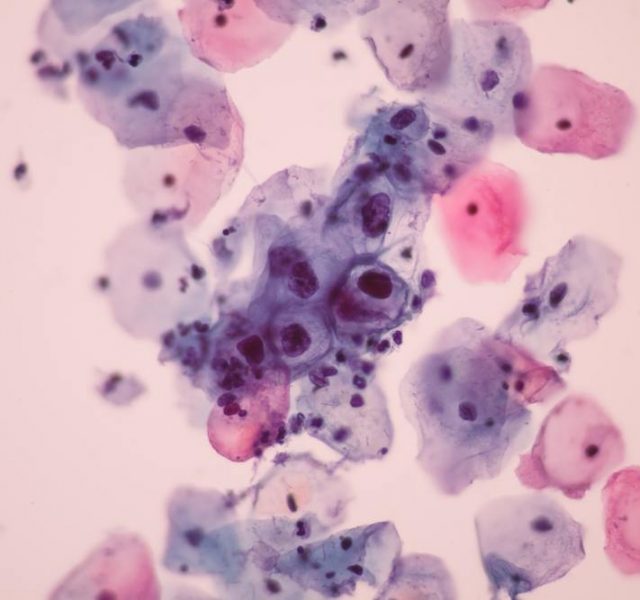
Genital warts are a clear sign of possessing HPV. However, this is not what should scare you as the cancer-associated typed of viruses do not cause the warts. Women should not disregard regular pap smears to check for abnormalities in cervix.
If there are any, your doctor might want you to perform an additional pap smear DNA test to identify the type of the virus. If the lab tests come positive for one of the cancer-associated types of viruses, usually type 16 and 18, the patient will require a special treatment.
HPV Testing In Men
No special testing is required for men as long as HPV does not cause significant health problems.
HPV Treatment. Is there a cure for HPV?
Medicine does not provide a special treatment for human papillomavirus infection and, luckily, most types of the infection do not cause harm to human body. However, women can be susceptible to serious conditions of the HPV, so they need to pay attention to treating it.
Human Papillomavirus Treatment for Men
Men normally do not suffer serious aggravations and do not require special treatment for HPV.
Human Papillomavirus Treatment for Women
If the virus, not associated with cancer, results in warts, a patient can opt to wait for them to go away without treatment or apply external medications, such as salicylic acid, imiquimod, podofilox or trichloracetic acid. Should the warts resist these medications, a patient may take decisive measures to eliminate the problem.
- Cryotherapy (removal using liquid nitrogen),
- Electrocautery (applying electrical current),
- Surgical removal and Laser surgery are all available.
If a woman has been diagnosed with abnormal cervical cells, she will need to be monitored by a doctor as they sometimes can develop into cervical cancer. It is important to control the progress of the infection as it can be cured relatively easy on early stages. In some cases a doctor will offer to eliminate the abnormal cells through cryotherapy, colposcopy or LEEP.
HPV Vaccines
Most HPV types are not accompanied by serious health issues and do not require special treatment. However, it might be a wise idea to get vaccinated against cancer-associated types of infection.
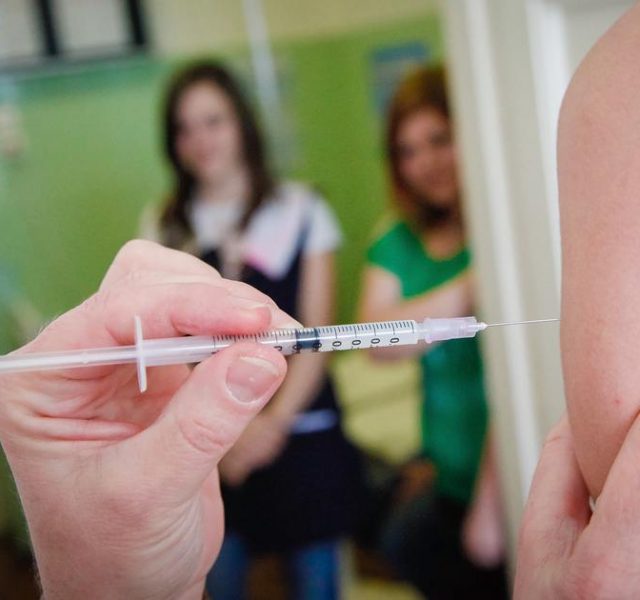
The first HPV vaccine, Gardasil, was patented in 2006 and protects against types 16 and 18 of the virus, responsible for cervical, throat and anal cancers, as well as those of vagina and vulva. It is recommended for both males and females aged between nine and twenty six.
Cervarix is another popular vaccine targeted at women aged 10–25. Doctors recommend giving the HPV vaccine to young people before the beginning of their sexual life as this is when they get exposed to most types of the virus.
Vaccine Safety
All available HPV vaccines protect against dangerous types of the virus that might end up in cancer, but may not affect the other random types. This means a person may still be exposed to HPV and have such symptoms as genital warts. It does not mean the vaccine is not working, and the symptoms are likely to go away without damaging your health. The vaccines do not contain the actual virus body, but a particle similar to the virus instead.
These vaccines proved to be safe and are recommended as a routine preventive measure for all young people. Pregnant women are the only exception. It is important for women not to discard the regular Pap smear tests after having taken the vaccine as it remains the main preventive measure in diagnosing many health abnormalities.
Vaccine Side Effects
No serious side effects of using HPV vaccines have been reported. Some people claim to have fainted after taking the vaccine. Short-term soreness in the area of injection is also common.
Read more about HPV Vaccine here.
If HPV is not treated
As we have said, HPV is a very common infection that occurs to over 50% of all sexually active people. It can have such symptoms as genital warts or not show any symptoms at all. That is why many infected people who do not pass medical tests on a regular basis have no idea of being infected. This is where the virus can develop into cancer. Women are more likely to be affected by the virus and can potentially develop cancer in cervical area, vagina, vulva or anus. This is why it is important to prevent virus development by regular Pap smears. Yet, in most cases the infection goes away without any treatment.
HPV Prevention
Prevention is always better than cure, and as long as HPV can potentially lead to cancer, it would be wise to take some simple steps to reduce the risk of falling to infection. The most effective and complex way is to be given a vaccine. It does not guarantee keeping the virus away from your body, but fights the most dangerous types of the infection, leading to cancers. They are most effective if given to young boys and girls before the beginning of sexual life.
Another preventive measure is having monogamous sexual relations. Once you are sure you and your partner do not have the virus and do not have other sexual relations, the risk of getting HPV is very low. Using condoms is another preventive measure, reducing the risk. Yet, the virus transmission remains possible. Be sure to wear slippers when in public pools and bathrooms. This will reduce the risk of getting plantar warts.
Read more about Human Papillomavirus Infection Prevention here.
FAQ
-
Is HPV curable?
There is no direct medicine to cure Human Papillomavirus. However, there are vaccines to prevent you from getting dangerous types of the virus and simple guidelines that can help you stay clear of the disease. If you have contracted the virus, there are several ways, including surgical, to get rid of the symptoms, such as warts. Serious cases, including cancer, need to have a complex medical approach.
Here you can find the list of curable and incurable STDs.
-
Does HPV go away?
HPV typically goes away on its own and does not require special treatment.
-
How long does it take for HPV to go away?
It is difficult to determine the average period of time required for the virus to go away from the body as it is usually unclear when it has been contracted. However, it can take as much as several years for the virus’ symptoms to go away after the moment they have been detected.
-
What causes HPV?
Human Papillomavirus stands for the large group of easily-transmitted viruses that potentially can cause cancer. They are usually transmitted during sexual intercourse, including oral, vaginal, anal sex and other skin-to-skin contacts. However, the infection can also enter someone’s body through any natural fluids or even minor skin cuts. HPV is one of the most spread sexually transmitted diseases.
-
Is HPV an STD?
Human Papillomavirus is a sexually transmitted disease as it is normally transmitted during sexual contacts. However, it should be remembered that it can potentially be transmitted via any skin-to-skin contact, even without sexual intercourse.