12 Common Communicable Diseases
 A communicable disease is one that passes from one person to another through contact with blood or body fluids, breathing in the germs released in air, or through insect bites. Some types of communicable diseases can also be transmitted indirectly by touching a surface covered with germs and by consuming contaminated food and water.
A communicable disease is one that passes from one person to another through contact with blood or body fluids, breathing in the germs released in air, or through insect bites. Some types of communicable diseases can also be transmitted indirectly by touching a surface covered with germs and by consuming contaminated food and water.
Some of the most common communicable diseases include:
Cold
 A cold is one of the most common types of communicable disease. The viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract affects the nose and results in stuffy or runny nose, sore throat, coughing, sneezing, and fever. Feeling of fatigue and lethargy are also associated with the ailment.
A cold is one of the most common types of communicable disease. The viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract affects the nose and results in stuffy or runny nose, sore throat, coughing, sneezing, and fever. Feeling of fatigue and lethargy are also associated with the ailment.
Since more than 200 viruses are responsible for the illness including coronaviruses or rhinoviruses, the human body can never build up sufficient immunity to block them. In fact, colds are so common and recurring that adults are reported to get them 2 -3 times per year while children have up to 12 colds per year.
The cold spreads by air droplets from coughs and sneezes of the infected individual. Touching an infected surface can also transmit the virus. The common cold becomes contagious a day or two before the symptoms appear and lasts until they stop.
Influenza or flu
Influenza, commonly known as the flu is a highly contagious illness that spreads by the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. You can also catch flu by touching the sick person.
Flu is similar to cold and is usually mistaken for the same. However, those who have flu also complain of:
- High temperatures
- Cold shivers
- Nausea, indigestion, and other gastrointestinal symptoms
- Muscular pain and tiredness
Normally, flu becomes contagious 1-2 days before the symptoms appear and lasts approximately 7 days after the person becomes ill.
Strep throat
 Strep throat is another disease that is similar to cold. It is caused by the group a streptococci bacteria and can be passed from one another through the sneezes and coughs of the sick person. Similarly, to cold and flu, you can also catch strep throat by touching the same surface as an infected person.
Strep throat is another disease that is similar to cold. It is caused by the group a streptococci bacteria and can be passed from one another through the sneezes and coughs of the sick person. Similarly, to cold and flu, you can also catch strep throat by touching the same surface as an infected person.
The symptoms of strep throat include pain in throat, difficulty swallowing, moderate to high fever, red and swollen tonsils, and small, red spots on the roof of the mouth. Strep throat remains contagious until the fever of the affected person subsides and they have started taking antibiotics for at least one day.
Pink eye
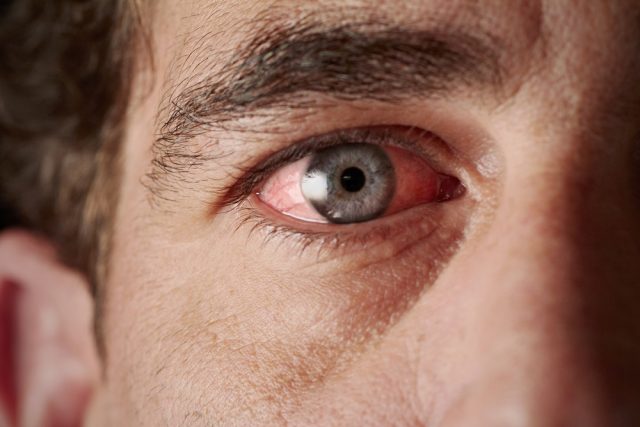 As the name implies, the pink eye is an infection of the eye. Also called the conjunctivitis, the pink eye occurs when the white part of the eye becomes inflamed and turns red or dark pink. The eye also appears swollen while watery or pus-type discharge is also common.
As the name implies, the pink eye is an infection of the eye. Also called the conjunctivitis, the pink eye occurs when the white part of the eye becomes inflamed and turns red or dark pink. The eye also appears swollen while watery or pus-type discharge is also common.
Several viruses contribute to the occurrence of pink eye including viruses’staphylococcus or streptococcus. Thebacterium passes from one person to another by coming into contact with the discharge through different means such as using the same towel or sharing eye makeup.
Contrary to the popular belief, pink eye is not caught by simply looking at someone’s infected. However, it can be transmitted through the sneezes or cough of the affected individual.
Gastroenteritis
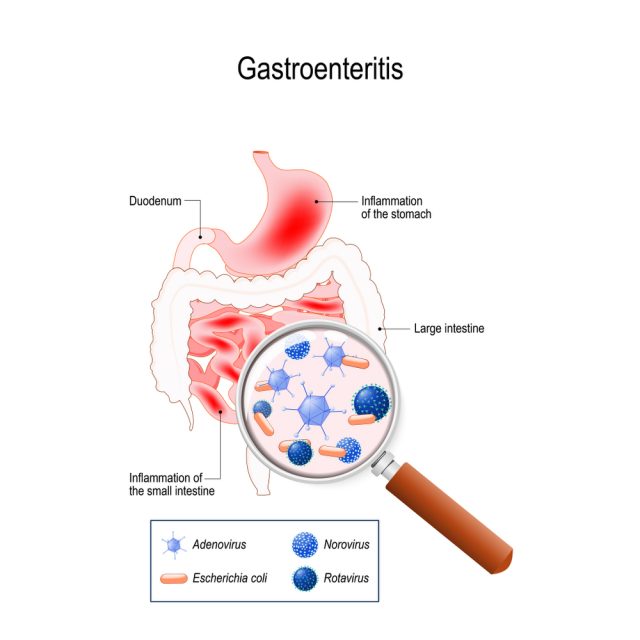 Called the stomach flu in non-medical term, the symptoms of gastroenteritis include cramps, diarrhea, vomiting, and nausea. Fever and dehydration are also common concerns of gastroenteritis.
Called the stomach flu in non-medical term, the symptoms of gastroenteritis include cramps, diarrhea, vomiting, and nausea. Fever and dehydration are also common concerns of gastroenteritis.
Norovirus and rotavirus are the main types of virus that causes the stomach flu. People become infected by directly touching the stool of the affected individual. It can also be transmitted by drinking or eating food from the same contaminated utensils.
Gastroenteritis usually resolves in 1 – 10 days. However, when it comes to its contagious-ability, the virus can spread for up to 2 weeks after the patient has fully recovered.
Fifth disease
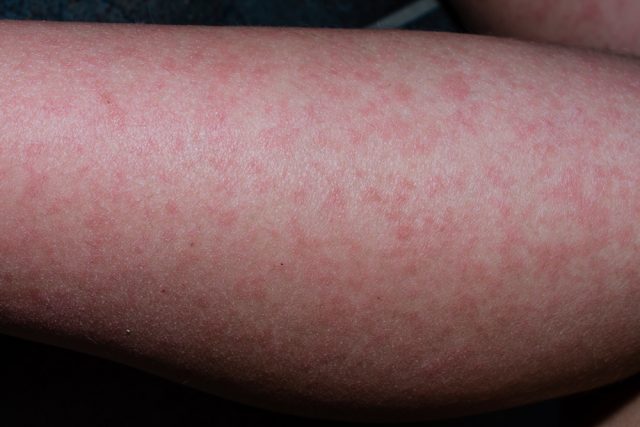 Another illness similar to cold and flu, the fifth disease produces the same symptoms as well. However, it is categorized by the appearance of rashes that appear in different parts of the body with the first being on the cheeks. It can also cause painful joints.
Another illness similar to cold and flu, the fifth disease produces the same symptoms as well. However, it is categorized by the appearance of rashes that appear in different parts of the body with the first being on the cheeks. It can also cause painful joints.
Fifth disease is common in children than adults and is a result of a virus called the parvovirus b19. It passes from one person to another in the same way a cold would but becomes noninfectious after the first rash appears.
Chicken pox
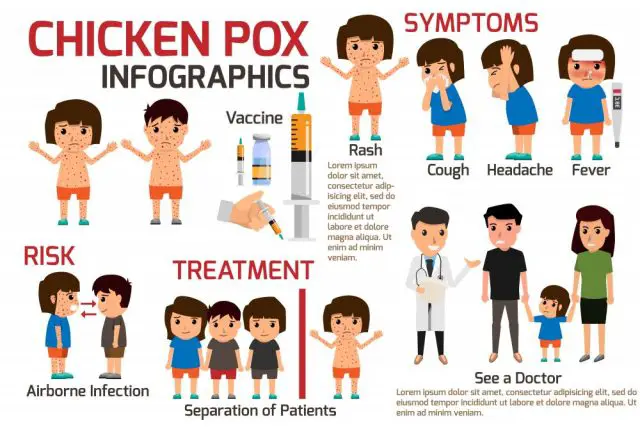 Chicken pox, also called the varicella is a well-known ailment. The symptom of chicken pox begins with rashes and small red blisters that gradually break open and crust. Fever and loss of appetite are also common symptoms of chicken pox.
Chicken pox, also called the varicella is a well-known ailment. The symptom of chicken pox begins with rashes and small red blisters that gradually break open and crust. Fever and loss of appetite are also common symptoms of chicken pox.
The varicella zoster virus is responsible for chicken pox. The communicable disease is transmittable by direct contact with the rash or breathing in the affected water droplets released from the open blisters. The person, infected with chicken pox is contagious before the first ‘itchy rash’ appears and remains well after the whole skin becomes clear. Since there is no treatment for chicken pox and the symptoms resolve on their own within a week or two, it is highly recommended to isolate the infected person to avoid spreading.
Chlamydia
 Chlamydia, a common sexually transmittable disease affects both – men and women. It is caused by the bacteria called the chlamydia trachomatis and spreads through sexual intercourse – even oral sex. The same can also be transmitted to the fetus if the mother is infected with the disease.
Chlamydia, a common sexually transmittable disease affects both – men and women. It is caused by the bacteria called the chlamydia trachomatis and spreads through sexual intercourse – even oral sex. The same can also be transmitted to the fetus if the mother is infected with the disease.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis or the TB is caused by the germs that attack the lungs. Unfortunately, if TB is not treated properly, it can become fatal. In fact, statistics show that over 2 billion of the world’s population is infected with TB while 9 million become sick with the ailment annually.
Tb spreads through the cough or the sneezes of an active TB person. Those who are in close contact with a TB-infected person can commonly catch the ailment.
It should be noted that tuberculosis does not spread by shaking hands, touching the same surface as the infected, and even kissing.
Herpes
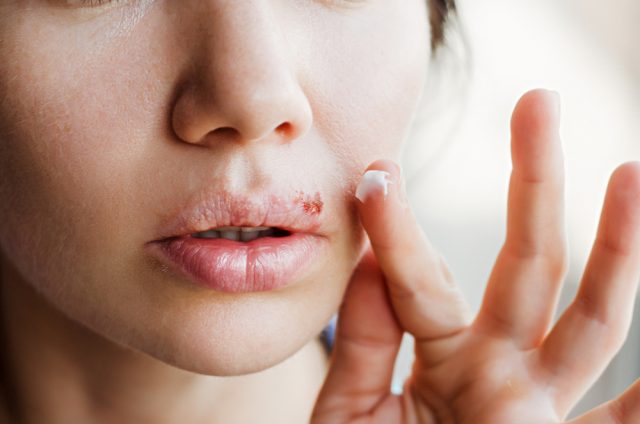 There are two main types of herpes: oral and genital. The symptoms of the ailment usually occur as sores located around the genital area or mouth. Both types of sores cause burning sensation and reappear even after the blisters crust over.
There are two main types of herpes: oral and genital. The symptoms of the ailment usually occur as sores located around the genital area or mouth. Both types of sores cause burning sensation and reappear even after the blisters crust over.
Herpes is caused by either herpes simplex virus type 1 or type 2. It spreads through contact with the saliva, the sides of the mouth, and kissing. Genital herpes is transferred by sexual contact.
As of yet, there is no cure for herpes except the use of topical medication. However, these ointments don’t kill off the bacteria from source and usually the symptoms reoccur.
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease that is common in areas with tropical and subtropical climates. It affects more than 500 million people annually and results in more than 1 million deaths annually. It is the second most common communicable disease and certainly one of the most deadliest.
Malaria is transmitted through female anopheles mosquito. It can also be transferred through blood infusion, organ transplant, and sharing syringes and needles. Malaria is also transmitted to an unborn baby through the infected mother. However, there is no way to get malaria through casual contact such as sharing the same air, sitting next to each other, and/or sexual intercourse.
Hepatitis b
 Hepatitis b is the most common infectious disease and is potentially life threatening. The disease causes inflammation of the liver that leads to jaundice, nausea, fatigue, and even long-term conditions such as liver cancer.
Hepatitis b is the most common infectious disease and is potentially life threatening. The disease causes inflammation of the liver that leads to jaundice, nausea, fatigue, and even long-term conditions such as liver cancer.
As of 2016, 27 million people were aware of the hepatitis b infection.
Hepatitis b is usually transmitted through the mother to her unborn child.it is also common through exposure of infected blood, sexual intercourse, and sharing used needles and syringes. Medical and dental procedures, tattooing, and piercing can also spread the infection.
Prevention of communicable diseases
Vaccines are usually available for some of the communicable diseases including flu, stomach flu, and hepatitis b. Ask your doctor about the preventive care and the vaccines available for the common ailments.
It is important that you follow proper hygiene to avoid catching the infection. Some tips to remember include:
- Covering the nose and mouth when coughing and sneezing
- Avoiding the share of towels, eye makeup, and even utensils
- Thoroughly washing the hands after using the toilet
- Using condoms during sexual intercourse
- Avoid sharing personal items such as razors, needles, syringes, and even toothbrushes
- Avoiding touching infected sores, blisters, and open wounds
- Always wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating
- Stay home and avoid going to work, school, or other public places to prevent spreading the infection when sick
Always remember, prevention is better than cure and practicing safeguard method is essential to protect oneself from these issues.
