Can You Get HPV from Kissing?
HPV or the Human Papillomavirus can be passed on during French kissing. French kissing involves open-mouth kissing. Other forms of oral sex such as mouth-to-genital or mouth-to-anus contact also lead to passing of this disease. It only transmits if one of the people is infected with HPV. It is the most common form of STD.
Can you get HPV from French kissing?
Tongue kissing and open-mouth kissing may lead to its transmission. This usually happens when one of the partners has oral HPV. But oral infections are uncommon and even if transmitted, they resolve on their own over a period of time.
They do not lead to mouth or throat cancer or other long term complications. Though most sexually active people have been exposed to this condition some time or the other during their sexual encounters, most of them do not come to know as the infection does not cause a major impact on their health.
Having oral sex with 6 or more partner increases your risk of catching neck and head cancers. Open-mouthed kissing with 10 or more partners increases the risk of HPV.
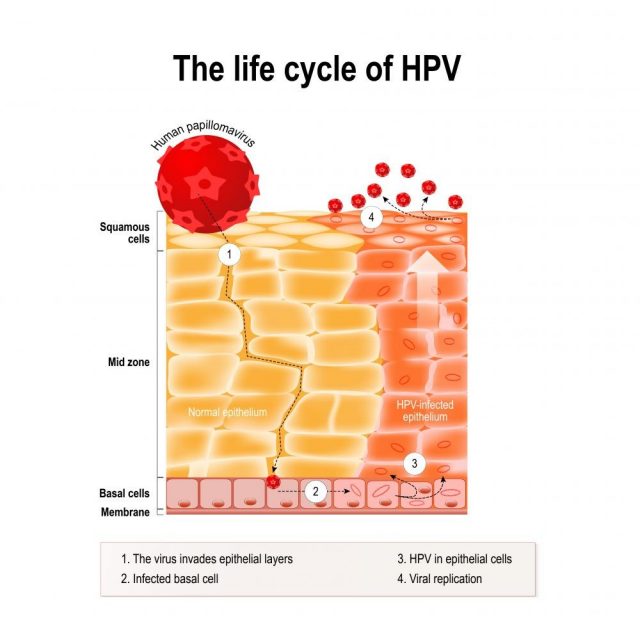
HPV virus
Human papilloma virus or HPV causes most types of vaginal, cervical and anal cancers. Cancer of the penis and vulva are also caused by it. Head and neck cancers have also been growing among men due to the infection.
There are 100 types of HPV but not all the strains are particularly cancer causing. HPV 16 and HPV 18 are considered to be the riskiest of all. The genital tract is full of the virus. A sexually active woman has around 70% chance of being infected by the virus around the age of 22.
But most of the time, the infection resolves on its own. Some infections which are not cleared by the immune system progress to disease. They may lead to genital warts or cancer. At such a time, sexual contact with an infected person may lead to transmission of the disease to the other partner. Men are more likely to be infected with oral infection when compared to women.
This condition when contracted by sexual contact does not become very active to cause visible symptoms. But when it increases beyond a certain degree, it invades the mucosal membranes covering the lining of the vagina, mouth, anus, cervix and throat. The area in and around these tissues can have warts eruptions due to this viral infection.
People in olden days used to presume that smoking or alcohol abuse was the only reason for oropharyngeal cancer. Today, cases of oropharyngeal cancers due to the virus are on the rise.
HPV And Tobacco
Tobacco was also found to increase the person’s chances of getting infected with HPV. The erosive nature of tobacco makes these infections less likely to clear of leading to higher risks of developing oropharyngeal cancers. Such people had higher risks of developing HPV 16 than those who never consume tobacco.
It waits for a wound to enter the body. Those who consume tobacco have a lot of openings or cuts inside their mouth. Poor oral hygiene such as inflammations, sores, ulcers in the mouth put these people at greater risks of contracting the disease.
Prevention of HPV virus
Deep kissing and oral sex can lead to its transmission from one person to another. The likelihood of contracting the infection increases by manifolds with the increase in the number of sexual partners. One should refrain from having multiple sexual partners and indulge in clean sex.
Oral sex can be done with the same partner but its better to get each other checked for any existence of STDs. A person who is infected from the virus should refrain from having sex till the condition is cleared.
Following mentioned are few ways of preventing HPV-related oral cancer if you are sexually active:
- There are vaccines available for the disease and pre-teens, teens and young adults should get these vaccines. Vaccination does not help people beyond their early 20s or those who have already been infected with it.
- According to a recommendation of the Centers for Disease Control, young women should get themselves vaccinated against cervical cancer.
- Young men should also get vaccinated to prevent the transmission to women and also to prevent the spread of 7000 types of HPV cancers occurring in men every year.
- Sexually active people can prevent the spread of this virus by using condoms during their penile-anal, penile-oral or penile-vaginal sexual encounters.
- A dental dam can also be used during oral-vaginal sex to prevent the spread of virus.
- If the person is diagnosed with an infection of the virus, then one should quickly get checked for related cancers immediately to improve the chances of cure. Possible symptoms may be:
- Persistent pain during swallowing or persistent sore throat
- Mouth sores or tongue sores which do not heal
- A lump in the neck which persists
Another prevention method is currently under exploration. It is the use of topical microbicides. Carrageenan is a compound which is extracted from seaweed and is also used in foods and some other products. It is found that this compound inhibits the virus spread in the laboratories. It is still under research, whether Carrageenan can prevent genital HPV infection or not.
Vaccines for HPV
The FDA has approved three vaccines for the prevention of the disease so far.
They are:
- Gardasil 9
- Gardasil
- Cervarix
All the 3 vaccines prevent infections spread by HPV types 16 and 18. These two are high-risk types and lead to HPV-related cancers. Gardasil prevents infections from its types 6 and 11 viruses which are responsible for 90% of genital warts.
Gardasil 9 prevents infection from its types 6, 11, 16, 18 and along with these four also prevent against five additional types which are also high risk-31, 33, 45, 52 and 58. Its vaccines not only provide protection against the mentioned types but also provide partial protection against a few other cancer causing HPV types. This phenomenon is called cross-protection.
These vaccines cannot prevent the spread of other common sexually transmitted diseases like STD and others. They are also incapable of treating existing viral diseases or infections. Since, they do not protect against HPV viruses causing cancer, women should undergo cervical cancer screening to rule out any possibilities of cancer.
These vaccines stimulate the body to produce antibodies which in future, if encounter the virus, will bind to the virus and stop it from infecting the cells in the body. These vaccines are effective against their target HPV type if given before an initial exposure to the virus.
Gardasil and Cervarix were found to be 100% successful in protecting against the persistent cervical infections caused by types 16 and 18 of the virus. Gardasil 9 is found to be 97% effective in protecting against vulvar, cervical and vaginal disease caused by virus types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58. The protection lasts for around 8 to 9 years. There are no serious side-effects of the virus and hence they are approved by the FDA as effective prevention against HPV.
Treatment
There is basically no cure or treatment for the virus as of now but research is on. One can get treated for the health problems resulting from HPV such as genital warts. Genital warts can be treated by prescription medication. If left untreated, they go away on their own, remain the same or increase in size or number.
The following medications can be taken to treat genital warts:
- Salicylic Acid: Over the counter topical applications can be applied to genital warts. These contain salicylic acid and they work by removing the layers of a wart little by little. Salicylic acid often leads to irritation and should not be used on the face.
- Imiquimod ( Aldara, Zyclara): This is a prescription cream which works by enhancing the body’s immune system to fight against the condition. This also causes some side effects like swelling and redness on the area of application.
- Podofilox: This topical application destroys the genital wart tissue and this also causes pain and itching on the application site.
- Trichloroacetic acid: This burns off the warts on the genitals, soles and palms and causes local irritation on some patients.
The following surgical procedures might be suggested by the doctor to remove warts:
- Surgical removal
- Laser surgery
- Burning of the warts using electric current. This process is called electrocautery.
Those who have a high-risk HPV, they would find abnormal changes in their cells that can be cancerous.
An abnormal PAP test result indicates further tests and treatment:
- Cryotherapy: In this treatment, the abnormal growth is frozen and the precancerous cells are removed from the cervix.
- Colposcopy: In this procedure, a detailed analysis of the cells in the cervix is done to find out whether they are cancerous or not.
- LEEP – Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure: In this treatment, precancerous cells are removed from the cervix via an electric current.