Causes of Testicle and Penis Pain
Introduction
If you’re feeling pain in your penis or testicles, you’re likely to start panicking. If you’ve started looking online, you’ve seen the stories of other men in your exact situation. That’s not exactly comforting though. In fact, it may lead you to worry even more and jump to worse-case scenarios. Yes, pain in your penis is unpleasant. Yes, it can be the sign of something serious. But, it’s likely to be nothing more than an infection or an irritation.
Every area around the penis can experience pain or discomfort. You can feel pain in the root of the penis, which is inside the shaft. You can feel pain in the shaft. You can feel pain in the head or the tip of the penis. You can feel pain in your urethra (the tube used to carry urine and semen). The most concerning area may be the testicles. Now, testicle pain varies from a strain to lack of oxygen. But don’t panic yet! Read on and find out what your symptoms sound like.
Then you can take a trip to the doctor and find out more about what’s going on.
Symptoms of Penis Pain
Naturally, the symptoms of penis pain vary. There are different conditions that cause different complications. As such, there are different symptoms. You may experience redness, itchy and trouble urinating. You may be fine, aside from an ache in the testicles. The generalized list below is just a guide to point you in the right direction. If you have any of these issues, make a note:
- Pain may develop slowly or be sudden and spontaneous
- Pain may be sharp, dull, throbbing/aching, mild
- Pain may be disrupting to daily activities
- Pain may cause issues with urination (including; pain when urinating, dribbling from penis, burning sensation when urinating)
- Penis or testicles may be swollen or red
- Penis or testicles may be tender to the touch
- Penis or testicles may be itchy
- Rash, sores or bumps may appear on and around the penis
- Inability to have intercourse (pain during intercourse, pain during ejaculation, pain when sexually aroused)
As you can see, there’s quite a variety of symptoms and none of them are very descriptive. These symptoms do require a trip to the doctor, but it’s not any type of medical emergency. Call your doctor and make an appointment as soon as possible. Make sure you mention every symptom you’re experiencing, even if you think it’s unrelated to the issue.
Unfortunately, there are other symptoms of penis pain that do require a trip to the emergency room. If you’re experiencing a high fever and a shooting pain in your testicles, you need to get to the emergency room immediately. Here are the other symptoms that should worry you:
- Inability to urinate at all
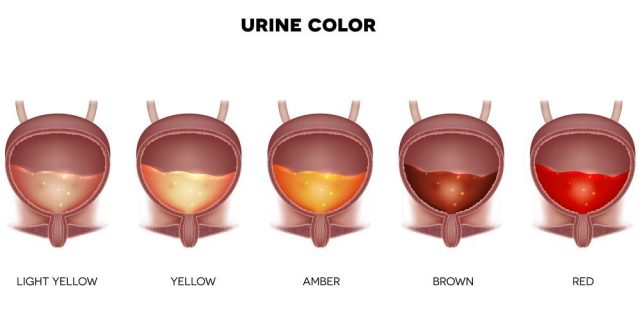
- Blood in the urine
- Erection lasting more than 4 hours
- Erectile dysfunction
- Popping or cracking sound during sexual arousal
- Discoloration of the penis
- Lumps on the penis or inside the penis
- Fever
- Any type of injury
Now that you are familiar with the symptoms of penis pain, it’s time to look at the causes. Below is a list of the different types of pain and what is most commonly the cause. This should help you to get a better understanding of what might be causing your pain.
The Various Causes of Penis Pain
It’s important to know the location of the pain, as that can be an indication of an underlying medical condition. Along with any symptoms you may be experiencing, it’s good to tell your doctor where the pain is. Let’s look at the locations of the pain and the most common causes;
The Tip
A burning or sharp pain at the tip of the penis is often the result of an irritation. This could be from a new brand of soap or shampoo you’re trying. The pain is common after urinating, but can occur more closely to the cause. You’ll want to wait a few days before heading to the doctor. If the pain goes away, it was nothing more than an irritation. You’ll want to ditch the soap or the lubricant or anything else that may have caused it.
An itching or general discomfort around the opening of the penis is often caused by chlamydia. This may be accompanied by painful urination or a burning sensation while urinating. However, the symptoms do not follow any type of regulation and may vary.
The Shaft
A priapism is defined as a “prolonged erection without stimulation”. This means that there’s no reason to feel excited, but that erection won’t go away. These erections are painful and persistent. This is actually the result of blood flowing improperly throughout the penis. The blood flows in, but isn’t flowing out correctly. A priapism can be caused by a number of variants, including; injury, diabetes, sickle cell anemia, damage to the central nervous system, CNS disorders, blood disorders, or leukemia.
Obviously, it’s important to rule out these causes. There is another reason that a priapism could occur. It’s often seen as a side-effect in patients that are taking performance drugs, like Viagra. This is especially true if those performance enhancing drugs are mixed with street drugs (eg: cocaine). You’ll need to get medical attention immediately to prevent permanent damage.
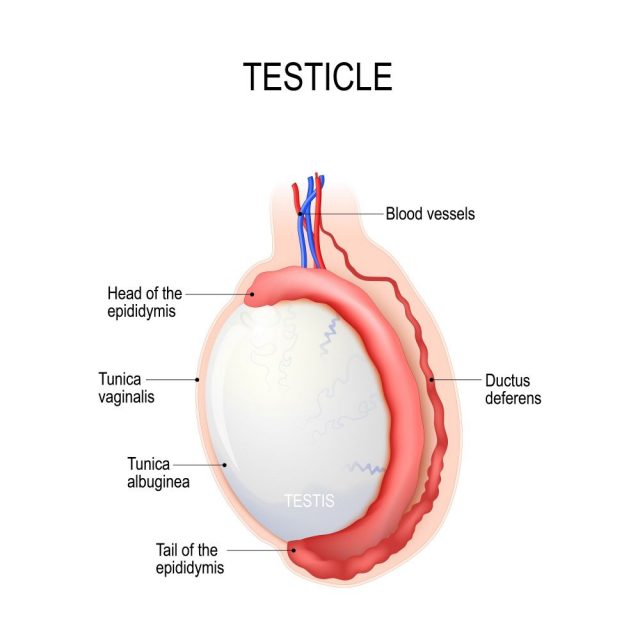
The Testicles
An aching in the ball sack, dull or heavy, is often the result of heavy lifting. Yes, your trip to the gym may have pulled something in your ball sack. If this is the cause, you’ll notice the pain lessens if you’re laying down on something soft, like a bed. You may even be able to trace your day back to the exact moments before you felt this aching. This could also be the result of an enlargement in your veins. This secondary cause does require medical attention, but it’s not immediate. If you leave it too long without medical attention, it could drastically impact your ability to reproduce.
A sharp pain shooting through your testicles is a medical emergency. This is often a sudden and pain that comes from nowhere. It’s immediate and may be accompanied by vomiting or nausea. If this is the case, it’s the result of something called testicular torsion. This is similar to a heart attack for your ball sack. When this happens, the oxygen is completely cut off. If you don’t get immediate medical attention, you may lose the testicle. You may never be able to have children as a result of dead tissue caused by the lack of oxygen.
A scrotal mass refers to a pain or tenderness in your testicles. This may affect one or both of the testicles. The most common cause for this type of pain is abnormal development of the tissue. It could also be the result of hydrocele or sac fluid around the testicles. Additionally, mumps or a mumps-like infection may cause the same tenderness. Testicular cancer may also be the cause of tender testicles.
A pain or swelling in the testicles may also be the result of an inguinal hernia. This happens when the intestines protrude into the scrotum. A hernia won’t always require medical attention, but this type certainly does. It can cause lasting damage if it isn’t treated as soon as possible.
The Base
A persistent aching at the base of the penis can be caused by epididymitis. This is a bacterial infection that doesn’t require more than an antibiotic to treat. Especially for individuals who are over the age of 35. Unfortunately, if you’re under the age of 35, there’s a chance this is caused by an STD.
Even if you think you’ve been practising safe sex, many STDs can catch you by surprise. It wouldn’t hurt to rule them out. This type of aching may become worse gradually and there may be redness and even swelling. If the symptoms get worse, you’ll want to head to the hospital. There’s a chance you may have a twist in the testicles.
General Pain
Of course, there are other STDs that cause trouble for the penis. Gonorrhea causes painful urination and often a burning sensation. Chancoid causes boils and sores around the base of the penis. Genital herpes appears more like blisters around the penis. If there are lesions and pain during intercourse, the cause may be the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Along with the causes above, there are other issues that may cause penis pain:
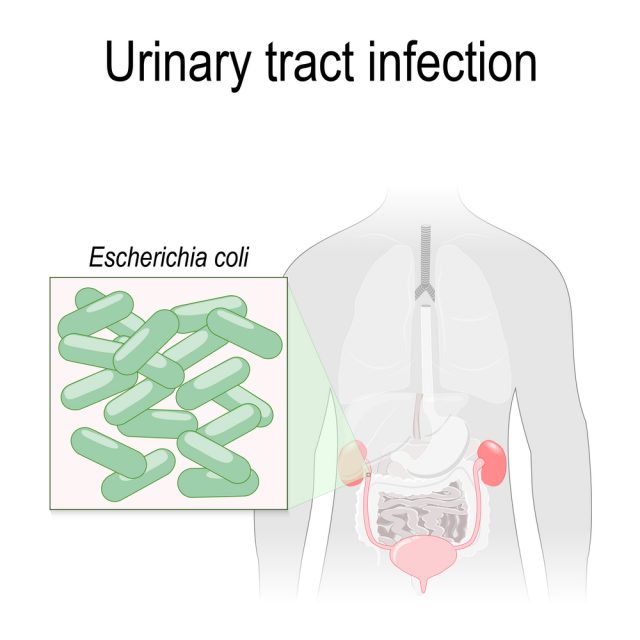
- UTI, urinary tract infection
- Balantis (infection under the foreskin)
- Allergic reaction
- Bladder/kidney stones
- Fractured penis
- Bite from animal or insect
- Acne or oily skin
- Poor personal hygiene
- Arthritis of the urethra
- Enlarged prostate
- Gangrene infections
If you feel there is something wrong with your genitals, seek medical attention. You want to know exactly what you’re dealing with so you’ll be able to treat the condition.
Diagnosis & Treatment of Penis Pain
There is no generalized list to diagnose or treat penis pain. This is simply because there are too many factors to consider. The treatment is entirely dependant on the cause of the pain. The only common treatment is an antibiotic to reduce the symptoms. Following an antibiotic, a number of steps may need to be taken from specialized testing to chemotherapy.
It is important to have a medical professional thoroughly diagnose your pain. This may involve a series of tests and it is important that you go for each one. Even if you feel the testing is irrelevant or unrelated. There is no such thing as playing it “too safe”.
This is your livelihood at risk.
Preventing Penis Pain
You should know what is coming next: Safe sex. It is extremely important that you are careful about all your sexual encounters. There are more STDs out there than you even know about. You don’t have to wrap yourself with plastic wrap, but you should take some precautions. This helps you to stay at peak health and helps to reduce the spreading of disease. If you don’t already know, there are STDs that you can get without coming into contact with someone else’s genitals. Bacteria can survive a little while outside of the body. This means if someone has recently touched themselves, they can pass an STD to you by touching you. Do you want to take that kind of risk?
Along with safe sex, personal hygiene is high on the list. This means bathing regularly and using body-friendly products. It also means going in for regular check-ups. Although you might not like your trips to the doctor, it could be beneficial. With any disease or infection, early detection makes a difference. The sooner you know something may be wrong, the sooner you can treat it. This reduces your risk for side-effects and long-term damage.
Here is a list of prevention tips, including the ones mentioned above:
- Safe sex
- Good personal hygiene
- Routine check-ups
- Limit excessive lifting
- Wear loose-fitting bottoms
- Wear a cup in high-risk situations