Chronic Epididymitis
Introduction
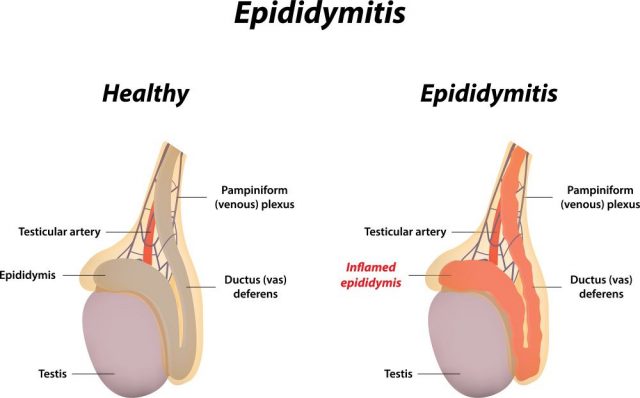
A good epididymitis definition is the inflammation of tube inside of your penis. This tube is called the epididymitis and it connects the testicles to the vas deferens. This tube is the same one that carries sperm. If there’s an inflammation of this tube, there’s an increased chance of infertility. Inflammation is the automated response to any perceived threat in the body. Typically, this type of inflammation is the result of a bacterial infection.
Acute epididymitis is a minor bacterial infection that lasts a maximum of 6 weeks, assuming the infection is treated with an antibiotic. Generally, the symptoms will ease after a short amount of time, but it’s important to take the antibiotic as described. Chronic epididymitis is an inflammation that continues to occur, even after it has been treated. This means epididymitis could last more than 6 weeks and the symptoms could become a problem to your every day lifestyle.
Epididymitis is the most common in men between the age of 14 and 35. However, it’s possible to get this type of infection at any point throughout life. In the younger age bracket, inflammation is usually caused by some sort of sexually transmitted disease. In older gentlemen, it’s nothing more than a foreign bacteria getting into the system.
Either way, it’s important to understand the causes and the treatments for epididymitis. You don’t want to guess on the cause because it could lead you to more serious complications.
Epididymitis Causes
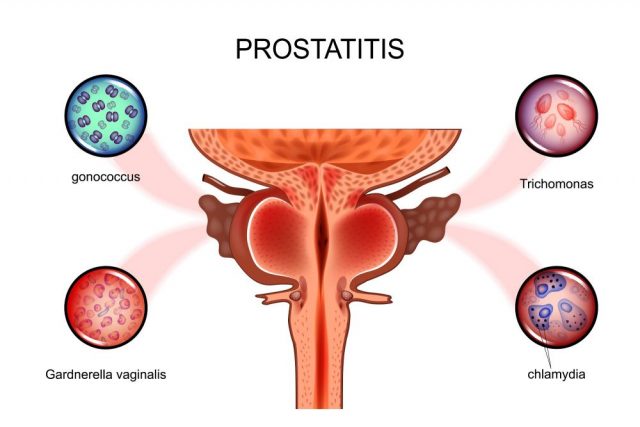
The two most common causes of epididymitis are STDs or an infection. The type of infection can vary from prostatitis to a urinary tract infection. As many people know, urinary tract infections are fairly easy to treat. There’s a chance antibiotics aren’t even required, though still recommended. Men who are uncircumcised are at a higher risk for infections.
Many other conditions can lead to epididymitis. This is just a short list of possibilities:
- An enlarged prostate
- Urinary tract infection
- Prostatitis
- Tuberculosis
- Heart conditions that require amiodarone to be taken
- STDs
Any infection caused by a sexually transmitted disease requires treatment. Here is a list of lifestyle choices that can affect the chances of getting epididymitis:
- A history of STDs
- Sexually active with multiple partners
- Not using protection during intercourse
- Poor personal hygiene
- Coming into contact with bacteria-rich environments
Additionally, there are some medical abnormalities that can place you in a higher risk bracket. These abnormalities include:
- Structural issues within the urinary tract
- Recent surgery to the urinary tract (for any reason)
- Groin injury
- Having used or using a urinary catheter
Now you can’t avoid all of these risks. Some of these risks may be with you from birth, such as physical abnormalities. The only thing you can control is your own activity. Ideally, getting checked on a regular basis will help you to catch any infection.
Epididymitis Symptoms
In most cases of epididymitis symptoms are minor. In fact, you may not even notice you’re experiencing symptoms at first. However, the symptoms will get worse the longer you wait to get medical attention. You can’t ignore these symptoms either. It could lead to serious complications in your future, including not being able to have children.
Here is a brief list of the side-effects you could experience:
- Swelling in testicles or any noticeable lump
- Pain in testicles or scrotum
- Redness or a warm sensation in scrotum
- Abnormal discharge from tip of the penis
- Painful urination or straining to urinate
- Burning sensation during urination
- Blood in urine
- Blood in semen
- Painful ejaculation
- Pain during intercourse
- Abdominal pain or pressure
- Chills
- Fever
If any of these symptoms are accompanied by a fever, you’ll need to seek immediate medical attention. Otherwise, you could get pretty sick. There are serious risks associated with epididymitis, so it’s important to get a proper diagnosis.
What Is Chronic Epididymitis
As mentioned earlier, epididymitis is considered chronic when the condition lasts longer than 6 months. Often, the inflammation won’t respond properly to treatment. However, both the symptoms and the bacteria can be kept under control with proper management techniques and antibiotics.
For cases of chronic epididymitis, the symptoms may not appear right away. They may come gradually or suddenly. You may only experience a few symptoms and go on with your life. You may also experience many of the symptoms and be negatively impacted. Your quality of life may decrease if your movement becomes limited or the bacteria becomes a serious problem.
It’s not known what causes chronic epididymitis. It seems to be random individuals that end up facing chronic symptoms. This means there isn’t a cure for chronic epididymitis as well. But there are methods to manage symptoms and that’s helpful.
Epididymitis Diagnosis
The first step to treating epididymitis is by diagnosing the infection. Your doctor will perform a complete physical examination. This is done to look for any obvious swelling and even discoloration. The doctor will also look to see if there is any type of discharge on or around the penis. If any type of discharge is present, a sample will be collected. Typically, this is done with a cotton swab. You won’t feel any pain if it’s a surface swab. Once taken, the sample will be sent for evaluation to determine the presence of bacterial culture. Some bacteria is expected, but there are strains that may indicate and infection. Following this physical exam, a number of other tests may be required:
- Urine sample
- Blood tests (largely to determine the blood cell count of both the red and white cells)
- Rectal examination
- Imaging tests (MRI, testicular ultrasound)
There is a condition that involves the infection spreading into the testicles. When this happens, it is refered to as epididymo-orchitis. Epididymitis is an inflammation in the penis, while orchitis is an inflammation in the testicles. It doesn’t sound pleasant, either way.
Once your doctor has determined the cause of your chronic epididymitis, it’s time to look at the possible treatments and methods to manage your symptoms.
Epididymitis Treatment Options
Initially, you will be given an antibiotic. You should notice the symptoms going away after 1-3 days. This applies whether you have acute or chronic epididymitis. In the instance of more severe cases, pain medication may be required. This is often morphine or codeine. Over-the-counter pain medication, like ibuprofen, may also be beneficial with any type of epididymitis. If your doctor doesn’t prescribe a pain medication, you can always grab a bottle of ibuprofen on your way home.
An anti-inflammatory medication should also be prescribed by your doctor or health care practitioner. There are many different options, but the most common choices are piroxicam (generically: feldene) and ketorolac (generically known as: toradol).
There are additional treatment options. The list below shares these options as well as recapping the treatments above:
- Antibiotics
- Pain medication
- Anti-inflammatory medication
- Surgery (if there is an abscess or blockage of any type)
- Home treatments
Surgery isn’t high on the list of treatments as it’s not typically helpful to epididymitis.
Epididymitis Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for epididymitis. This is because it has almost instant results. Plus, it helps to fight the bacteria that has infected your groin. Typically, antibiotics are administered for at least 4 weeks. They may be given up to 6 weeks as well, depending on improvement. There are two main antibiotics prescribed:
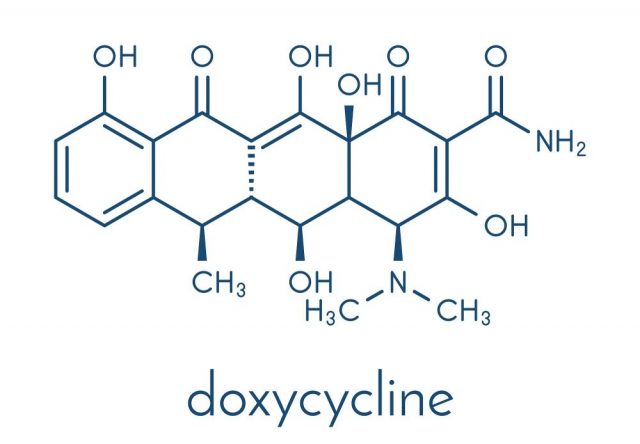
- doxycycline
- ciprofloxacin
Depending on which one you are given, there is a chance you will need to ask your doctor to switch. Many people respond better to a certain antibiotic than they do to others. You may even need to be prescribed a different antibiotic altogether. Typically, doxycycline is the most effective, being prescribed to many individuals who suffer from chronic epididymitis.
Even if you are feeling better, you should stick to the instructions your doctor gave you. Many medications require proactive treatments in order to truly take effect. You can also learn to manage your chronic epididymitis with home treatments, as detailed below.
Epididymitis Home Treatment
Many people are looking for alternative solutions to medications. While medication may be required in some cases of epididymitis, chronic epididymitis has room for home remedies. This is because they are basically intended to manage symptoms, not eliminate the infection. Those with chronic epididymitis are unlikely to be rid of the infection.
These home treatments are bound to help you manage the symptoms of chronic epididymitis:
- A glass of real cranberry juice, at least 3 times a day to flush out the infection and eliminate bacteria

- Turmeric tea, 3 times a day, can be used to reduce pain and swelling (turmeric tablets can be used in a similar fashion)
- Mix garlic cloves into your meals for use as an antibiotic
- Mix oregano oil into your meals to effectively kill bacteria

- Chew yarrow plant leaves or a yarrow supplement for multiple benefits
These aren’t your only options for home treatments though. Below is a list of 4 herbs that you can use to make your own home treatment for chronic epididymitis. Each of these herbs can be taken individually or used in conjunction with any of the other herbs listed. The correct dosage is 1 tablet, 3 times a day. If you’re choosing a liquid dropper, it’s 1 full dropper, 3 times a day.
- Cleavers – This is ideal for lymphatic congestion as it improves the urinary flow
- Black cohosh – This is typically ideal for pain management
- Uva ursi – This is an antibacterial herb that can help to reduce the infection
- Goldenseal – This is only intended to be used for 14 days and largely only used when the epididymitis is caused by a urinary tract infection
These home treatments are meant to manage symptoms of chronic epididymitis. You cannot substitute a doctor’s opinion for home treatments. You can use these home treatments after you know what the proper diagnosis is. Although they are typically pretty safe, you should always talk to your doctor before taking any home remedy. Especially if you are also taking any type of medication. There are some medications that have negative reactions to herbal remedies.
Home treatments for epididymitis are ideal when the condition is chronic. They aren’t necessary when the condition is acute. Home treatment does nothing for cases of epididymitis that are caused by STDs.
There are other methods for managing chronic epididymitis, which include:
- Get plenty of rest and limit your movement
- Elevate your scrotum as needed
- Apply an ice pack to the groin
- Apply a heating pad to the groin
- Wear a protective cup when participating in any high-risk event
- Avoiding heavy lifting or constant lifting
- Abstain from sexual intercourse when symptoms are present
- Consistently practice safe sex
- Check-in with your doctor every 6 months
The Risks of Epididymitis in Left Untreated
Similar to many other conditions, getting treatment is crucial. Epididymitis can cause serious risks if it’s left untreated. These complications include:
- An abscess in the scrotum
- Fistula (an abnormal passage in the scrotum)
- Reduced blood flow leading to the death of tissue in the testicles
- Shrinkage of the testicles
- Inability to procreate
Regardless of the severity of your symptoms, you should always seek medical attention for penis pain. You may not need to rush to the emergency room, but it doesn’t hurt to get a check-up. You should book preventative testing for every 6 months. This gives you the chance to catch anything that might start stirring and prevent the risk of serious developments.
There are also support groups online that can connect you to others who suffer from chronic epididymitis. This can help you to understand any emotions you might be feeling. It can be a bummer to have to limit your lifestyle because of some infection. Also, you’ll benefit in being able to find new methods of managing symptoms and get support from a community of individuals in the same position as you.