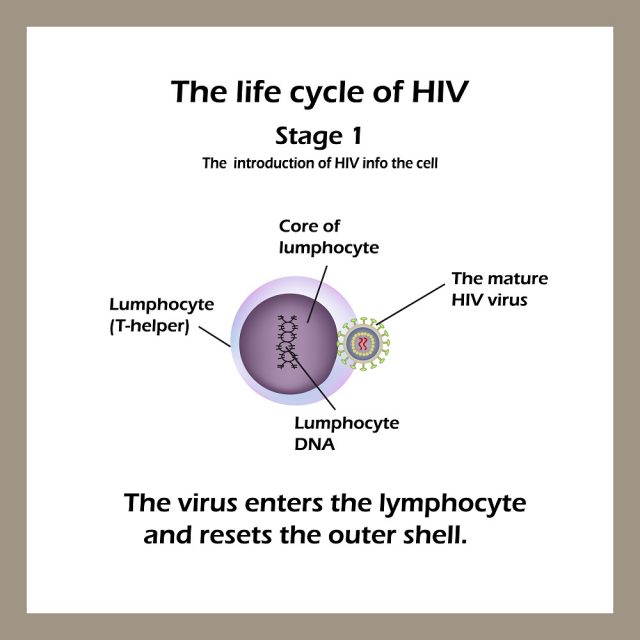
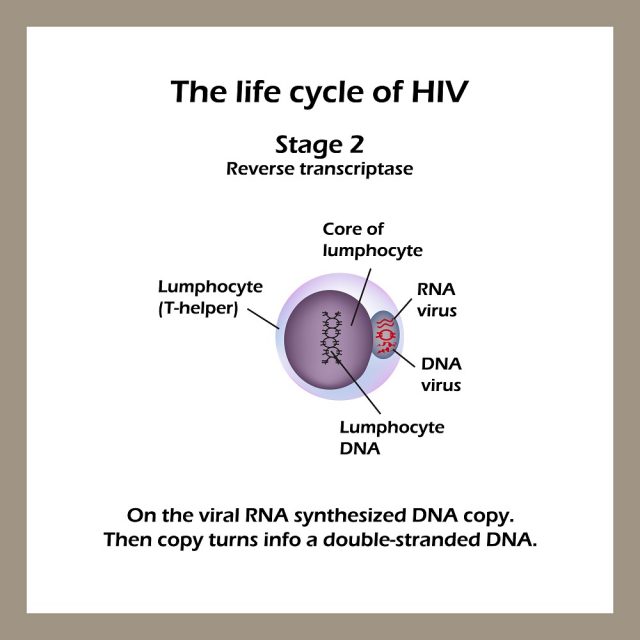
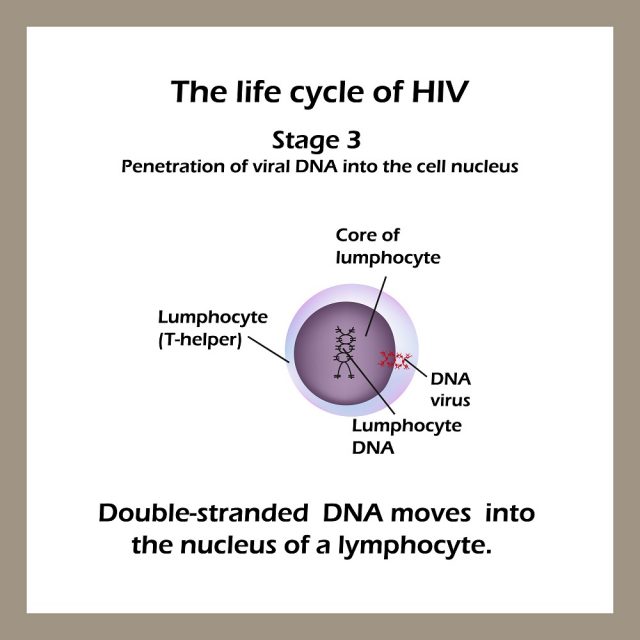
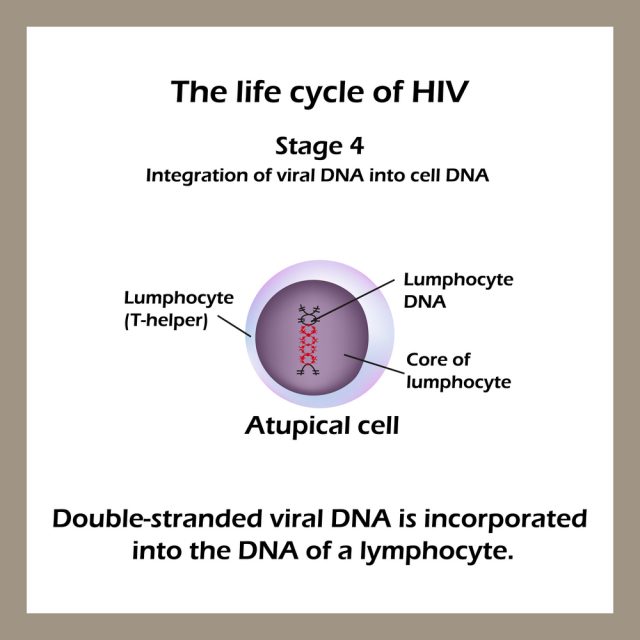
Stages of HIV & AIDS
HIV virus spreads in the human body through certain kind of fluids that have a major impact on the immune system; especially on CD4 cells that are usually named as T cells. Studies reveal that HIV can destroy most of these cells with time and the human body loses its ability to fight off common infections and diseases.
T cells in the human body are responsible for boosting the ability of immune system to deal with illnesses. When a person is infected with HIV virus, it starts reducing the number of CD4 cells in his body, and this damage in the body makes it harder for the immune system to handle diseases and infections. In this way, the opportunistic infections including cancer, etc. take advantage to attack patient’s body and it leads to severe discomfort. The sad fact is that there is no cure available for HIV infection; all that you can do is follow some precautions and remedies to slow down the impact. The effective medical care can help to control the discomfort up to some extent. One of the most popular medicines that are used to treat HIV is named as antiretroviral therapy. If this treatment is taken in right way, it can help to increase the life cycle of people affected by HIV and also keep them healthy with lesser chances of infecting others. AIDS is the last phase of HIV infection; it happens when immune system in patient’s body gets badly damaged, and the opportunistic infections take over.
Different stages of HIV & AIDS
If you do not get appropriate treatment, HIV keeps on advancing to different stages, and they make the performance of immune system worse over time. The three different stages of HIV infection are acute HIV infection, clinical latency, and AIDS. As discussed above, there is no cure available for HIV, but the good news is that it is possible to delay the progression from HIV to AIDS. Antiretroviral therapy is capable enough to help patients live longer and also reduces the risk of virus transmission to other bodies. Below we have included few essential details about three different stages of HIV infection:
Stage 1: Acute HIV Infection
Many people live a long time without any recognizable symptom of HIV infection; however, others report a flu-like symptom even within 2 to 4 weeks after infection. The common symptoms of the disease may include a headache, pains, joint aches, muscles, rash, sore throat, swollen glands, and fever. This condition is often named as Primary HIV Infection or Acute Retroviral Syndrome (ARS), and it is the natural response of body towards HIV infection. Patients that are recently infected with HIV infection are advised to consult medical health professionals to avail right care on time. If the treatment begins at the beginning of this stage, it can lead to significant health benefits in the long run and can also increase the life expectancy of the patient.
Studies reveal that at an early stage of infection, huge amounts of viruses get produced in the body and target the CD4 cells in the immune system. In this process, the number of essential CD4 cells gets reduced, and the immune response of your body also falls down to a level marked as a viral set point. Although production of CD4 cells starts increasing at this point, they are not able to reach the pre-infection level. Medical health professionals advise using antiretroviral therapy at this stage to avoid further complications. At this stage of the virus, the patient is able to transmit HIV infection to his/her sexual partner, or it can also transfer to another body via infected blood transfers.
Common symptoms of disease at first stage of HIV infection include:
- Muscle pain.
- Joint pains and aches.
- Upset stomach.
- Headache.
- Swollen glands.
- Sore
- Body rash.
- Fever
Stage 2: Clinical Latency
After the first stage of HIV infection, a disease in your body steps ahead to the second stage that is named as Clinical Latency stage. The word latency here means that virus is living inside the body without producing any recognizable symptom. It means, at the second stage, patients infected with HIV suffer no serious complication or may notice mild issues.
Medical health professionals reveal that at this stage, HIV virus continues to reproduce at slightly low levels and it cannot be even detected in clinical tests. In case if you receive antiretroviral therapy on time, it is possible to live with clinical latency stage for several years as it helps your body to stop the virus from progressing to the final stage of infection. Even in this symptom-free stage, patients are able to transfer the virus to others; however, the risks can be greatly reduced by using appropriate treatment. People that are not availing antiretroviral therapy suffer from this second stage of HIV infection for almost 10 years, but few patients reported faster progress in their body. With the progress in diseases, the viral load also increases in your body, and the count of CD4 keeps on decaying to a large extent. Patients may also develop several constitutional symptoms with the progress in disease.
When the patient starts developing symptomatic HIV infection by the end of clinical latency stage, he/she may face severe discomfort due to:
- Serious illnesses.
- Regular infections.
- Skin and mouth problems.
- Persistent
- Fever
- Night sweats.
- Chronic diarrhoea.
- Weight loss.
Stage 3: AIDS
Here is the final stage of HIV infection and it can be recognized from the condition when the immune system of patient get affected badly. The opportunistic infections and viruses become highly active in the body, and it increases the level of discomfort. As per medical health professionals, the time when the count of CD4 cells falls below the level of 200 cells/cubic mm of blood, the patient enters to the last stage of the disease. The last stage is also identified as a severe illness that is caused by one or more opportunistic illnesses.
If you do not take antiretroviral therapy on time, it is possible to survive hardly for only 3 years with this stage. In case if your body is damaged by certain severe illness, the life expectancy may reduce to one year only. That is why medical health professionals advise taking right treatment on time to delay the last stage of the disease. Some studies on patients in the United States reveal that people who take antiretroviral therapy on time are able to live longer with HIV infection as compared to those who do not take any treatment.
-
Early stage AIDS:
In this stage, the immune system of patient’s body becomes susceptible to few mild fungal, viral and bacterial infections. The mild symptoms at this point may include night sweats, fatigue, skin rashes, slight weight loss, nail and skin infections. Some people also report fatigue and headache at this stage of AIDS.
-
Middle stage AIDS:
The middle stage can be identified from the severity of infections. As per medical health reports, a person may suffer some fungal infections in vagina or mouth area with the development of some yellow or white colored film that causes irritation. The common symptoms observed by patients at middle stage AIDs include major weight loss, diarrhea, cold sores in genitals and mouth, persistent fevers.
-
Late stage AIDS:
At this point in time, the patient spends most time dealing with serious medical health issues. The most commonly reported infections include cytomegalovirus, pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, Mycobacterium avium complex disease. The symptoms reported by patients at late stage AIDS include depression, memory loss, intense night sweats, diarrhea, and related brain disorders. With time, the patient may also develop Kaposi’s sarcoma, a typical type of cancer that causes the development of brown, red and purple blotches on the skin surface.
There are so many factors that are responsible for the progress of the disease in patient’s body; it may include the genetic makeup, health conditions before infection, early virus exposures and many more. It is important to stay in touch with medical healthcare service providers and follow their instructions to stay safe. At the same time, one should make efforts to improve overall lifestyle including diet habits, and exercises.
HIV testing is important to know if the person is affected with HIV or not. You can take this test at any recognized medical health center nearby, and the reports are kept confidential by experts. If the test is negative, it means you don’t have HIV; in this case, it is better to follow appropriate precautions to avoid the disease for a lifetime. Prefer to use condoms during sex, and in case if you feel yourself at high risk of getting infected, it is better to take preventive medications on time.
In case if HIV test shows that you are infected with HIV, it is time to take appropriate steps to protect your overall health. the very first thing you need to do is start taking antiretroviral therapy to treat the infection. These medications are essential to slow down the overall impact of disease so that you can live a happy life for a longer time. Make sure you stay in touch with a trustworthy medical health professional at every stage of the disease.