Hepatitis C

What is Hepatitis C
The term “Hepatitis” is used to define an inflammatory condition of the liver. Among the triggers for hepatitis are some meds, toxins, certain diseases, alcohol abuse, bacterial and virus infections etc. For the moment there are 5 known hepatitis types: A, B, C, D, E.
Hepatitis C shall be taken to be the most virulent type. The existence of this hepatitis type was confirmed in 1989. It’s estimated that about 3% of people worldwide are subject to chronic hepatitis C. Around half a million people decease annually from liver diseases provoked by hepatitis C.
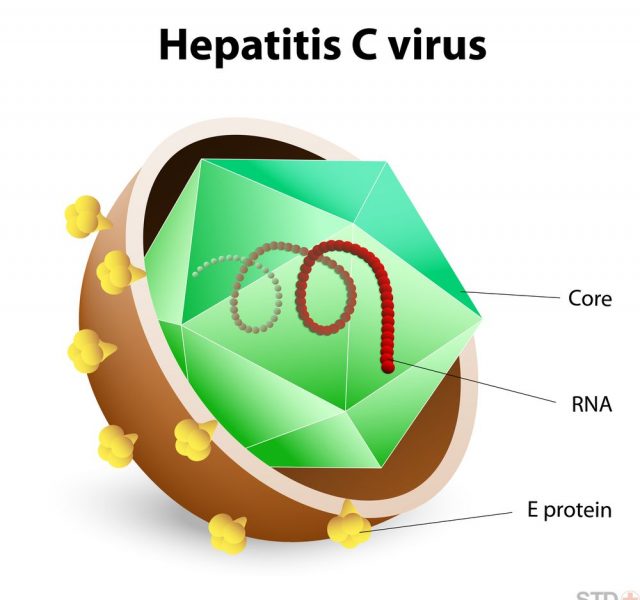
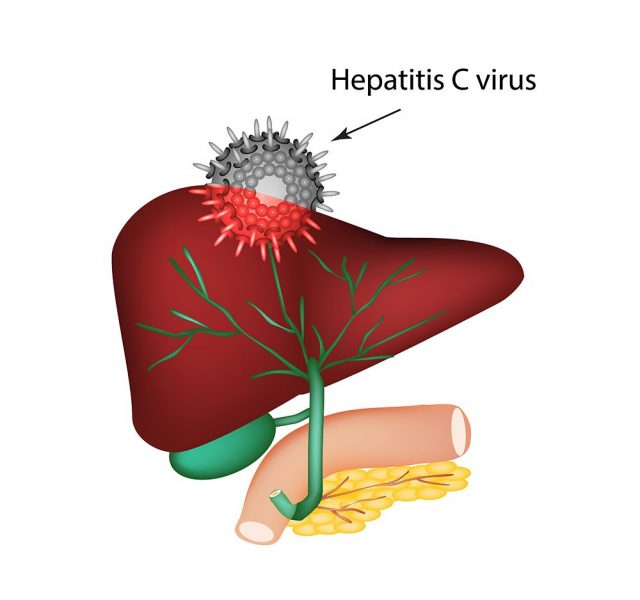
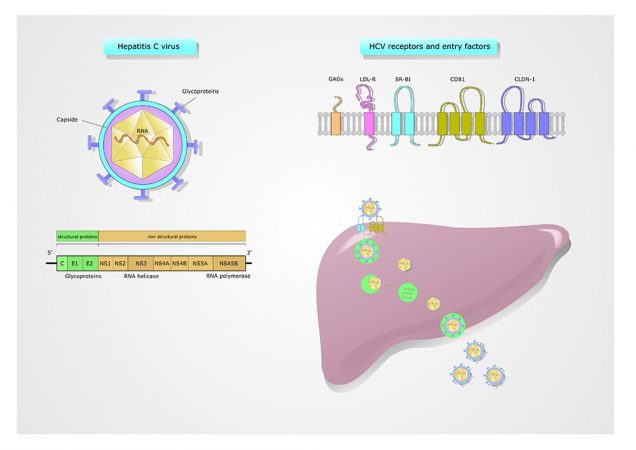
Hepatitis C is a contagious disorder influencing the liver and resulting from the hepatitis C virus. It can come out in mild cases that last no longer than few weeks as well as the serious ones enduring diseases that strike the liver. Basically the virus invades due to blood-to-blood contacts with the infected people.
The disease can be “acute” as well as “chronic.”
Acute condition is a short-run illness that develops within half a year after the exposal to the Hepatitis C virus. Typically acute infection triggers a chronic one.
Chronic HCV infection is a continuing disease that occurs provided that the virus stays in the human body. It can be a lifetime condition leading to severe conditions such as cirrhosis or liver cancer, normally appearing years after the initial contracting.
Causes
- Viral infection. Most Hepatitis cases are related to viral infection that is transmitted from infected persons.
- Transmission from pregnant mother to the child.
- Alcohol, drugs, medications and other toxins. Various toxins and poisons may cause liver inflammation, swelling and eventual disease.
- Autoimmune system failure. Sometimes the body starts producing antibodies that destroy liver tissue due to some immune failure.
Key Facts
Hepatitis C is a hardly determinable disease that may not show any symptoms in many cases.
Following the WHO data, about 3% of the world population is HCV-infected and there are more than 170 million chronic index cases risking developing liver cirrhosis and/or liver cancer.
Hepatitis C is passed from mom to her baby in 6% of cases. The risk for children to be infected is much higher if the lying-in woman has both HIV and Hepatitis C.
The virus can not be passed through meals, water or casual contact.
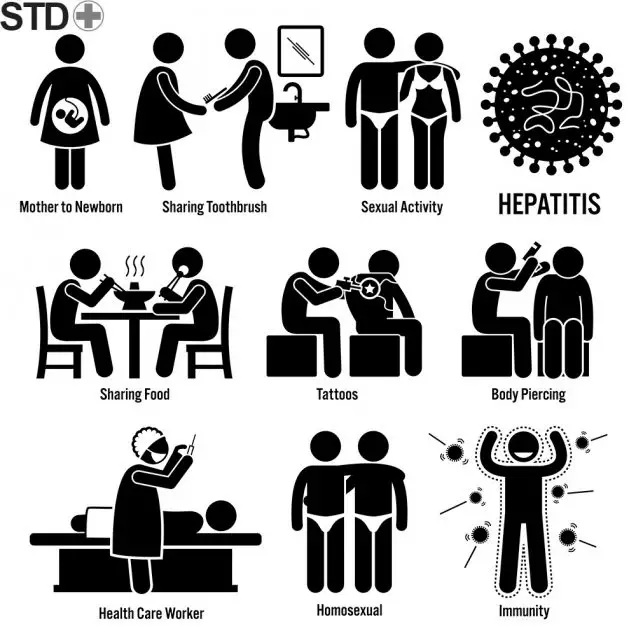
How is Hepatitis C Transmitted?
The virus is transmitted through blood or biological liquid of an infected person.
If you share drugs or needles, have unprotected sex, rough sex or many sexual partners you are at risk group. You should also get tested if you were subject to hemotransfusion or organ transplantation, continuous kidney dialysis or were born from a Hepatitis C positive woman.
Symptoms of Hepatitis C
The latent stage for the disease is 2 to 26 weeks. 80% of cases are asymptomatic. Meanwhile high temperature, weakness, appetite loss, nausea, vomiting, tummy pain, dark urine, pale bowel movements, arthralgia and jaundice can be among the acute symptoms.
Testing and Diagnosis
2 steps are required to diagnose HCV infection:
Screening assay for anti-HCV antibodies along with a serological test permit to diagnose if a person has been infected. Positive HCV antibodies test demands further study in order to confirm chronic infection because in up to 45% of cases the immune system can defeat the infection. After this the liver damage degree needs to be evaluated in order to find the right treatment. Apart from biopsy there is a range of non-invasive methods permitting to make an assessment.
The genotype of the stain should also be identified because each of 6 genotypes should be treated differently. Moreover there are some genotypes combinations demanding appropriate medication.
In the course of the treatment you’ll be monitored and checked with different blood tests, imaging tests and biopsy.
Treatment of Hepatitis C
The result of successful treatment is disposing of the virus and it’s heavily related to the stain of the virus and treatment type. Getting rid of the virus can cause a complication like a liver damage resulting in hepatic failure or liver cancer. Medical care is indispensable for those having signs of liver fibrosis or scarring.
Modern hepatitis C treatment varies a lot from the one practiced a few years ago. A single daily shot of Harvoni, which is much safer and better-tolerated than earlier medications, is able to cure the disease in 8–12 weeks in most cases. Harvoni comprises two drugs: sofosbuvir and ledipasvir. However this medication is quite expensive and has a range of side effects like fatigue and headache.
It is worth saying that this disease doesn’t always demand treatment because of the immune response that is capable of clearing the virus. Until recent times interferon and ribavirin had to be used during 48 weeks to overcome the disease, and this kind of treatment only yielded favorable results in 50% of cases, while grave side effects were possible.
Medications
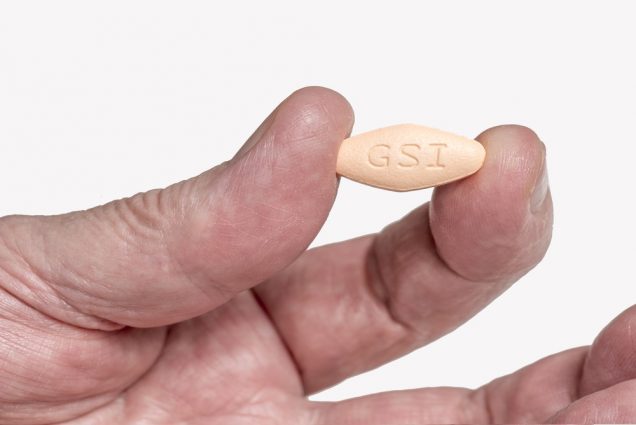

SAN DIEGO, CALIFORNIA; JULY 7, 2016 : HARVONI medicine treatment of Hepatitis C. A pill costs 1,000 US dollars in the US. Harvoni made by Gilead Sciences, California, USA
Among the most widespread HCV medications are Boceprevir (Victrelis), Ribavirin, Sofosbuvir, Simeprevir, Simeprevir and Harvoni. Some of them have severe side effects.
For example, Ribavirin use can potentially result in birth defects so the patients should practice safe sex in order to avert pregnancy at least during first half a year after the treatment.
At the same time it should be mentioned that the next generation drugs like Harvoni are much safer and efficient.
Surgery
Hepatitis C can culminate in liver transplantation due to cirrhosis. In up to 30% of cases, cirrhosis is developed within five years. Such treatment option can lead to some surgical complications. However the survival rate is high enough — about 73% of people can live with a transplanted liver up to 5 years.
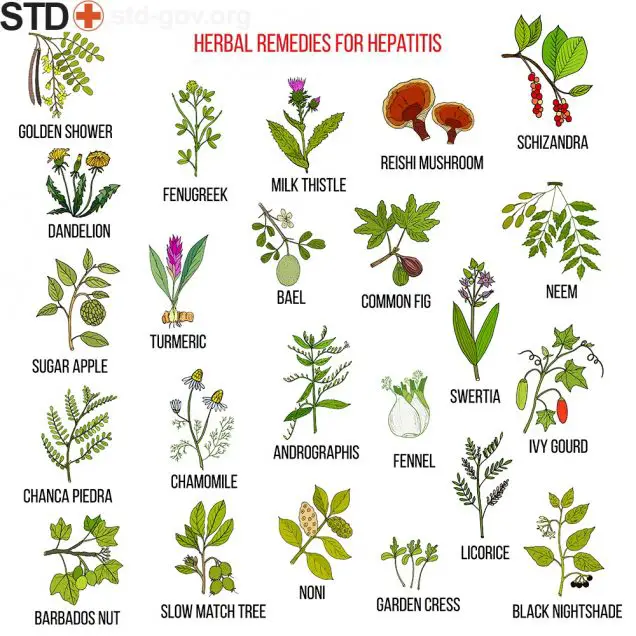
Alternative Medicine
There is quite a popular belief that some alternative medications can be helpful in curing the Hepatitis C virus. Among these alternative remedies and methods are milk thistle, colloidal silver, acupuncture, supplements containing zinc, ginseng, probiotics etc. In the meantime this kind of treatment can also cause side effects and there are no confirmations of treatment efficacy.
Hepatitis C Prevention
There is still no vaccine against this disease. The one way to avoid it is to lessen the risk of infection at most.
The most common precautionary measures are:
- Hand hygiene including the use of disposable gloves and hand washing, especially during medical interventions;
- Correct condom use;
- The use of your own shaving accessories;
- Avoiding blood-to-blood contacts.
If you are already infected you should get immunized with the hepatitis A and B vaccines so you can prevent coinfections, choose an appropriate medical care and monitor your condition on an ongoing basis.
If you are not treated
If a patient doesn’t undergo appropriate treatment the virus can cause unacceptable health risks.
HCV can result in liver scarring or cancer and finally the liver can stop functioning. However modern treatments allow to get rid of the virus and most of the patients have a normal life expectancy and can lead an ordinary life.
If you start treating hepatitis C early on, you’ll manage to reduce complicating disorders.
FAQ:
Is there a cure for Hepatitis C?
The cure for Hepatitis C exists but the biggest problem about the next generation medications that can cure the disease in a short period of time is the price. Unfortunately, this kind of medications is not affordable for most people. Pharmaceutical companies keep the prices high and the mortality rate is still significant. At the same time the appropriate treatment on early stages is of primary importance.
What are the Hepatitis C side effects?
The most frequent effects caused by drugs curing hepatitis C are:
- Influenza-like symptoms
- Weakness
- Hair loss
- Low blood counts
- Trouble thinking
- Agitation
- Depression
- Anemia due to hemolysis
- Cough
- Nausea
- Short breathing
- Insomnia
- Appetite loss