Vaginal Yeast Infection
What is Vaginal Yeast Infection?
Candida albicans is a diploid fungus that grows both as yeast and filamentous cells and a causal agent of opportunistic oral and genital infections in humans
A naturally occurring fungus called Candida albicans (C. albicans) usually causes this type of vaginitis. An estimated three out of four women will have yeast infection in their lifetime.
Many of you probably know vaginal yeast infection as candidiasis. It is considered to be absolutely normal condition for women. It is named so due to the fact that vaginal yeast infection can be caused by fungus candida. It is usually followed by several unpleasant side effects including swelling, irritation and itching.
The latest medical researches show that 3 out of 4 women may get vaginal yeast infection at a particular point of their lives regardless of age. In addition women are very likely to have more infections in future. It usually occurs more than once.
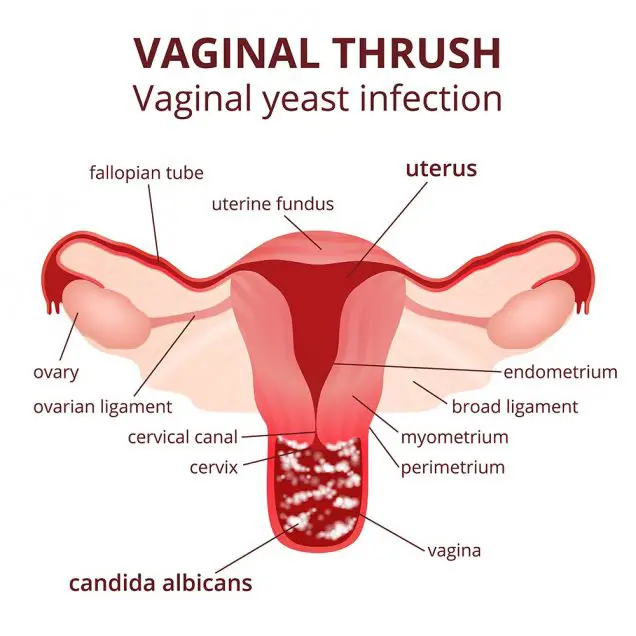
Female reproductive system, the uterus and ovaries scheme vulvovaginal candidiasis or vaginal yeast infection
The infection spread by various ways including sexual contact. On the other hand this infection does not belong to sexually transmitted diseases. Patients will hardly face any difficulties in treating vaginal yeast infection. Still it will depend on the level of disease severity.
How is it contracted?
Apart from causing most vaginal yeast infections, Candida albicans (C. albicans) also causes infections in other moist areas of your body, such as your mouth (thrush), skin folds and fingernail beds. The fungi can also cause diaper rash.
Factors that increase your risk of yeast infections include:
- Medications such as antibiotics and steroids;
- Uncontrolled diabetes;
- Hormonal changes, such as those associated with pregnancy and birth control pills;
- Bubble baths, vaginal contraceptives, damp or tight- fitting clothing and feminine hygiene products such as sprays and deodorants don’t cause yeast infections, but they may increase your susceptibility to infection.
Incubation Period
Anywhere from 12 hours to five days.
Symptoms of Vaginal Yeast Infection
The main symptom is itching, but you may have white, thick discharge that resembles cottage cheese.
At the same time there are some other common symptoms and side effects of vaginal yeast infection. You should note that severity of symptoms depends on the length of untreated period. In other words if you leave it without any treatment for a long period of time it may have a negative effect and lead to more serious health problems. That is why you are recommended to consult your doctor in the following cases:
- burning;
- itching;
- vaginal discharge (even if you notice small amount of discharge it may be the first sign of yeast infection occurrence. It has grey color and thick consistency. In some cases discharge can also be watery);
- painful feelings while having sex with your partner;
- soreness;
- rash and swelling.
Common Causes of Vaginal Yeast Infections
Vaginal yeast infection is mainly caused by candida genus which is natural microorganisms that can be found in vaginal areas. The growth of these microorganisms depends on lactobacillus bacteria. In other words if bacteria balance is normal, nothing serious will happen. As soon as the balance changes, it creates perfect environment for yeast infection occurrence. It means that there is misbalance in your system. Such conditions result in yeast overgrowth which leads to yeast infection symptoms.
The majority of infections can be treated rather easily and fast. However, conventional treatment can be of no use in some cases. It means that the main cause of infection is hidden in other types of candida genus. In such situation additional laboratory tests and analysis are necessary in order to receive correct diagnosis. You need to consult your healthcare provider and start treatment course as prescribed.
Yeast overgrowth may be caused by the following:
- antibiotic medications (they sometimes may reduce the number of healthy bacteria and lactobacillus which are necessary for balance);
- pregnancy;
- chronic diseases including diabetes;
- poor operation of immune system;
- douching;
- eating unhealthy food with big amount of sugar;
- menstrual cycle followed by possible hormonal misbalance;
- tiredness, stress and lack of sleep.
Testing for Vaginal Yeast Infection
In the majority of cases it is rather easy to diagnose yeast infection. First of all a doctor will get acquainted with information contained in your medical history. It will help to determine whether patient already suffered from various infections which may also include sexual transmitted diseases.
Testing may include several steps depending on the severity of infection. After necessary information from your medical history is obtained, it is high time to proceed with the next stage. It includes pelvic exam. Doctor usually tests the area around vagina to determine any possible signs of infection.
Thorough testing also deals with examination of vagina walls and cervix. Further steps will depend on discoveries of your doctor. He will take vaginal culture to proceed with laboratory tests in case of necessity to make correct diagnosis. This is especially important when the woman is pregnant. Your doctor may take a sample of a cervical or vaginal discharge for laboratory analysis.
If yeast infection occurs for the first time, such testing may turn out to be a good background to determine its presence in future.
Vaginal Yeast Infection Treatment
Yeast infection treatment depends on the level of severity.
When it comes to simple infection, doctors usually prescribe several common cures:
- antifungal cream, tablet or ointment. Treatment should be taken from 1 to 3 days until all yeast infection symptoms are gone;
- single dosage of Diflucan.
Patients with simple infection should regularly check with their healthcare provider till the treatment course is completed. It is necessary to ensure the medication has positive effect.
Complicated yeast infection calls for more efficient treatment and additional analysis. This is due to the fact that there are some candida types that will not respond to common ways of infection treatment. In this case patients need more aggressive medication course. The level of infection complexity may be identified under the following symptoms:
- swelling, redness, itching;
- having over 4 yeast infections per 1 year;
- pregnancy;
- chronic and uncontrolled diseases such as diabetes.
In case any of the abovementioned symptoms occurs, a patient needs more aggressive treatment course which may include:
- 14-day cream usage, ointment or tablets;
- increase of Diflucan dosage by 2 or 3 times depending on severity(not recommended for pregnant women);
- parallel treatment of your sexual partner;
- use of condoms during coitus.
Antibiotics — Diflucan 150 mg one single dose.
If you are not treated
Generally, vaginal yeast infections don’t cause serious complications. If it is not treated the itching may persist.
At the same time if traditional treatment did not come in handy, you can also try several popular alternative methods. On the one hand it will make it possible to avoid taking prescribed drugs. On the other hand you can do it at home without visiting your doctor.
Common alternative methods include:
- using vinegar douches or garlic;
- yogurt or tea tree oil cream inserted in vagina.