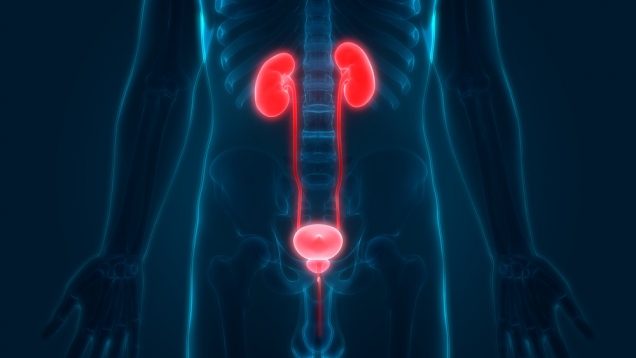
Painful Urination (Dysuria)
Painful Urination is a fairly common disease, especially among sexually active people and young women. Dysuria results from various reasons starting from infections of all kinds to ectopic pregnancy as well as emergencies like appendicitis. Painful urination can be accompanied by dribbling or changes in color or amount of urine.
The most frequent causes of painful urination
Bladder Stones
Bladder Stones are solid buildups of minerals that arise because of retained urine or foreign objects in the bladder. Sometimes bladder stones do not come out in any symptoms but normally the disease is characterized by severe lower abdominal or back pain and pressure, difficult and/or frequent emiction at night, fever, burning or pain in the urethra when urinating, blood in the urine or loss of urine control.
STDs and STIs (Chlamydia, Genital Herpes, Gonorrhea, Vaginitis, Yeast Infection)
The symptoms of STDs and STIs vary from person to person but discharge, sharp sensation when urinating and sores are among the most widespread symptoms. Chlamydia for example can often run asymptomatically while Genital Herpes causes painful blisters and sores, Gonorrhea causes discharge, pain or bleeding during or after sex and pain while urinating and Yeast Infection comes out in irritation, abnormal discharge and sharp itchiness of the vagina.
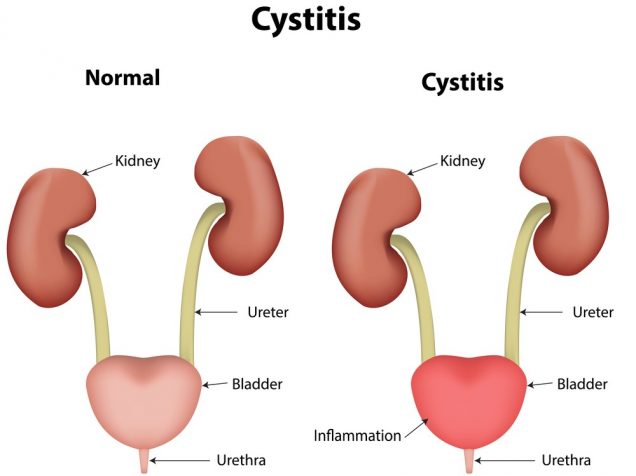
Cystitis
Cystitis is an infection affecting the lower urinary tract, coming from inflammation of the bladder and causing symptoms such as cloudy, smelly or bloody urine, soreness in the reins and in the abdomen, pressure or discomfort in the bladder and pelvic region.
Drugs
Dysuria can be a bad effect from meds, supplements or treatments such as cyclophosphamide, danazol, anti-inflammatory remedies or anticholinergic medication.
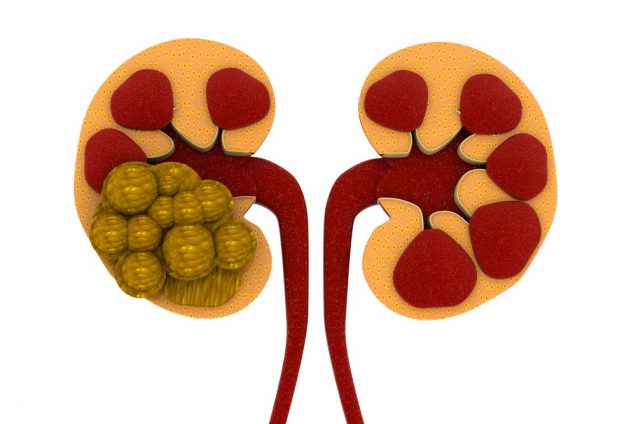
Kidney stones
Kidney stones are hard mineral materials formed within the kidney or urinary tract. Small kidney stones may even go undetected but bigger ones can cause fever, chills, flank pain, hematuria and nausea. The ureter blocked by a Kidney Stone can give rise to a Kidney Infection that comes out in cloudy and bad-smelling urine, shivering, chills, weakness and diarrhea.
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is an inflammation state of the prostatic gland most often evoked by a bacterial infection. It can be an acute or a chronic condition. Prostatitis can be characterized by genitourinary pain, sexual dysfunction and general health problems, similar to flu symptoms.
Painful urination can also arise from mechanical irritation due to the vaginal ring or diaphragm or medical procedures involving the use of urologic instruments. Chemical irritants such as lubricants, personal hygiene products, contraceptives, tampons or even toilet paper can also cause dysuria. The reason for dysuria can also lie in other diseases such as Radiation cystitis, Urethral stricture, Urethritis or Tumor in the urinary tract.
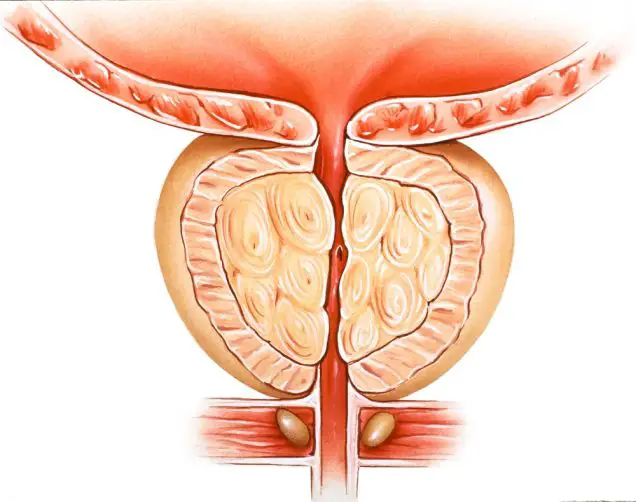
Prostate – (BPH) Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia or BPH, prostate growth affects virtually all men over fifty
What to do in case of Painful Urination (Dysuria)
Some people can feel mild discomfort while urinating. Normally this discomfort doesn’t pose any threat to your health. However, if painful urination happens with regularity or you’ve got other symptoms like stinging sensation while peeing, blood or pus in urine etc., it is a sign to see the physician. After general surveying you’ll most probably have to be analyzed for STDs and STIs, undergo ultrasound or X-ray, urine cytology and other laboratory tests.
Test results will normally allow to prescribe some optimal medications. If an infection is a prevailing cause of dysuria, antibiotics will most probably be prescribed. If it becomes clear that the cause of painful urination has nothing in common with any infections, further tests will be performed.
How to treat Painful Urination
Treatment for dysuria is reliant on the cause of the disorder. Only knowing the cause of abnormal urination allows the doctor to prescribe adequate medication.
Therefore, for example, urinary tract infections (UTIs) are normally treated with antibiotics. However, it’s worth remembering that only the full course of antibiotics can guarantee complete cure. If the inflammation is caused by any kind of skin irritation, first thing you need to do is to get rid of the irritator. Whatever the treatment is, it is imperative to obey the instructions of your doctor.
FAQ:
I have pain while urinating during pregnancy. What should I do?
Pregnancy makes women more amenable to UTIs because of all the changes undergone by the body that create conditions for the bacterial growth. If frequent urination is a natural occurrence during pregnancy, experiencing any kind of discomfort or pain is a problem and a sign of an STI or an UTI that may lead to kidney infection. Kidney infection is highly dangerous for pregnant women because it may be the cause of advanced labor or low birth weight. If UTIs are diagnosed at early stages, they can be treated properly without any harm to the baby. Even if your symptoms are mild, you should contact your physician in good time in order to have your urine tested. In case of any infections, a course of antibiotics safe for the fetus will be prescribed. In severe cases you may be hospitalized and monitored.
What should I do if I have sharp pain during urination after intercourse?
Pain during urination after sex can indicate an allergic reaction to a specific kind of condoms, lubricant or spermicide. Therefore, you can try changing contraceptives and lubricant in order to check up if the reason of the pain is allergy.
Painful urination after sex may also occur if your bladder is full during intercourse. Having sex with an empty bladder can help to resolve the problem.
Mechanical irritation within the intercourse may also lead to dysuria — it is a result of so-called honeymoon cystitis. Compression on the urethra during sex and vaginal dryness can bring on pain too.
Anyway, whatever the reasons for this kind of pain are, it is highly recommended to pee and wash the genitals after sex in order to rinse off bacteria.
It cannot be excluded that sharp pain can point at the presence of an infection which makes a visit to a doctor a sensible move.